Interactions count: plant origin, herbivory and disturbance jointly explain seedling recruitment and community structure
- PMID: 28811574
- PMCID: PMC5557803
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-08401-3
Interactions count: plant origin, herbivory and disturbance jointly explain seedling recruitment and community structure
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Interactions count: plant origin, herbivory and disturbance jointly explain seedling recruitment and community structure.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 8;8(1):4399. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22518-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29520066 Free PMC article.
Abstract
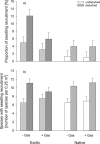
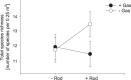
Herbivory and disturbance are major drivers of biological invasions, but it is unclear how they interact to determine exotic vs. native seedling recruitment and what consequences arise for biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Previous studies neglected the roles of different, potentially interacting, guilds of generalist herbivores such as rodents and gastropods. We therefore set up a full-factorial rodent exclusion x gastropod exclusion x disturbance x seed-addition experiment in a grassland community in Central Germany and measured early seedling recruitment, as well as species richness, species composition and aboveground biomass. Gastropod herbivory reduced the positive effect of disturbance on seedling recruitment, particularly for exotic species. Rodent herbivory had weak positive effects on seedling recruitment at undisturbed sites, irrespective of species origin. This effect was likely driven by their strong negative effect on productivity. Interactive effects between both herbivore guilds became only evident for species richness and composition. How many species established themselves depended on disturbance, but was independent of species origin. The fewer exotic species that established themselves increased productivity to a stronger extent compared to native species. Our study highlights that joint effects of disturbance, herbivory and species origin shape early recruitment, while they only weakly affect biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Mueller G, Horstmeyer L, Roenneburg T, van Kleunen M, Dawson W. Alien and native plant establishment in grassland communities is more strongly affected by disturbance than above-and below-ground enemies. J. Ecol. 2016;104:1211–1218. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12619. - DOI
-
- Sakai, A. K. et al. The population biology of invasive specie. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Sys., 305–332 (2001).
-
- Grubb PJ. The maintenance of species-richness in plant communities: the importance of the regeneration niche. Biol. Rev. 1977;52:107–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.1977.tb01347.x. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

