Sex-dependent difference in the effect of metformin on colorectal cancer-specific mortality of diabetic colorectal cancer patients
- PMID: 28811714
- PMCID: PMC5537186
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5196
Sex-dependent difference in the effect of metformin on colorectal cancer-specific mortality of diabetic colorectal cancer patients
Abstract
Aim: To assess factors associated with the higher effect of metformin on mortality in diabetic colorectal cancer (CRC) patients, since the factors related to the effectiveness of metformin have not been identified yet.
Methods: Between January 2000 and December 2010, 413 patients diagnosed with both stage 3/4 CRC and diabetes mellitus were identified. Patients' demographics and clinical characteristics were analyzed. The effect of metformin on CRC-specific mortality and the interactions between metformin and each adjusted factor were evaluated.
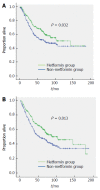
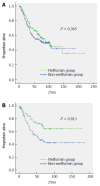
Results: Total follow-up duration was median 50 mo (range: 1-218 mo). There were 85 deaths (45.9%) and 72 CRC-specific deaths (38.9%) among 185 patients who used metformin, compared to 130 total deaths (57.0%) and 107 CRC-specific deaths (46.9%) among 228 patients who did not use metformin. In multivariate analysis, survival benefit associated with metformin administration was identified (HR = 0.985, 95%CI: 0.974-0.997, P = 0.012). Interaction test between metformin and sex after adjustment for relevant factors revealed that female CRC patients taking metformin exhibited a significantly lower CRC-specific mortality rate than male CRC patients taking metformin (HR = 0.369, 95%CI: 0.155-0.881, P = 0.025). Furthermore, subgroup analysis revealed significant differences in CRC-specific mortality between the metformin and non-metformin groups in female patients (HR = 0.501, 95%CI: 0.286-0.879, P = 0.013) but not male patients (HR = 0.848, 95%CI: 0.594-1.211, P = 0.365). There were no significant interactions between metformin and other adjusted factors on CRC-specific mortality.
Conclusion: We showed a strong sex-dependent difference in the effect of metformin on CRC-specific mortality in advanced stage CRC patients with diabetes.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Metformin; Sex; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Lim D, Ha M, Song I. Trends in major cancer mortality in Korea, 1983-2012, with a joinpoint analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015;39:939–946. - PubMed
-
- Sung JJ, Lau JY, Goh KL, Leung WK; Asia Pacific Working Group on Colorectal Cancer. Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer in Asia: implications for screening. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:871–876. - PubMed
-
- Vigneri P, Frasca F, Sciacca L, Pandini G, Vigneri R. Diabetes and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009;16:1103–1123. - PubMed
-
- Coughlin SS, Calle EE, Teras LR, Petrelli J, Thun MJ. Diabetes mellitus as a predictor of cancer mortality in a large cohort of US adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;159:1160–1167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

