Multimodal Neuroimaging in Schizophrenia: Description and Dissemination
- PMID: 28812221
- PMCID: PMC5671541
- DOI: 10.1007/s12021-017-9338-9
Multimodal Neuroimaging in Schizophrenia: Description and Dissemination
Abstract
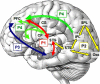
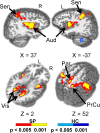
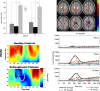
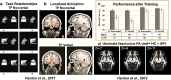
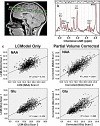
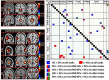
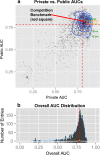
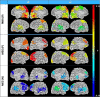
In this paper we describe an open-access collection of multimodal neuroimaging data in schizophrenia for release to the community. Data were acquired from approximately 100 patients with schizophrenia and 100 age-matched controls during rest as well as several task activation paradigms targeting a hierarchy of cognitive constructs. Neuroimaging data include structural MRI, functional MRI, diffusion MRI, MR spectroscopic imaging, and magnetoencephalography. For three of the hypothesis-driven projects, task activation paradigms were acquired on subsets of ~200 volunteers which examined a range of sensory and cognitive processes (e.g., auditory sensory gating, auditory/visual multisensory integration, visual transverse patterning). Neuropsychological data were also acquired and genetic material via saliva samples were collected from most of the participants and have been typed for both genome-wide polymorphism data as well as genome-wide methylation data. Some results are also presented from the individual studies as well as from our data-driven multimodal analyses (e.g., multimodal examinations of network structure and network dynamics and multitask fMRI data analysis across projects). All data will be released through the Mind Research Network's collaborative informatics and neuroimaging suite (COINS).
Keywords: COBRE; COINS; DTI; Genetics; ICA; MATRICS; MEG; Magnetoencephalography; Memory; Multimodal integration; Neuroimaging; Schizophrenia; Sensory gating; Spectroscopy; Transverse patterning; fMRI.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott CC, Merideth F, Ruhl D, Yang Z, Clark VP, Calhoun VD, Hanlon FM, Mayer AR. Auditory orienting and inhibition of return in schizophrenia: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2012;37:161–168. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2011.12.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adler LE, Pachtman E, Franks RD, Pecevich M, Waldo MC, Freedman R. Neurophysiological evidence for a defect in neuronal mechanisms involved in sensory gating in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 1982;17:639–654. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

