eDGAR: a database of Disease-Gene Associations with annotated Relationships among genes
- PMID: 28812536
- PMCID: PMC5558190
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-3911-3
eDGAR: a database of Disease-Gene Associations with annotated Relationships among genes
Abstract
Background: Genetic investigations, boosted by modern sequencing techniques, allow dissecting the genetic component of different phenotypic traits. These efforts result in the compilation of lists of genes related to diseases and show that an increasing number of diseases is associated with multiple genes. Investigating functional relations among genes associated with the same disease contributes to highlighting molecular mechanisms of the pathogenesis.
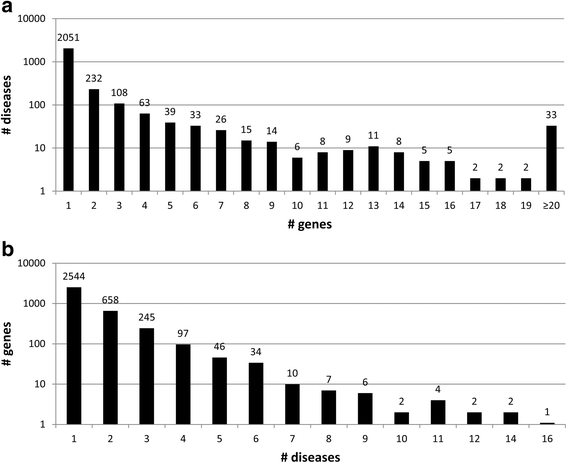
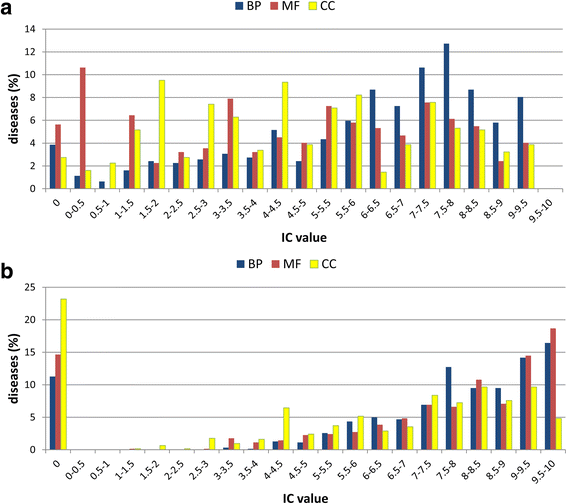
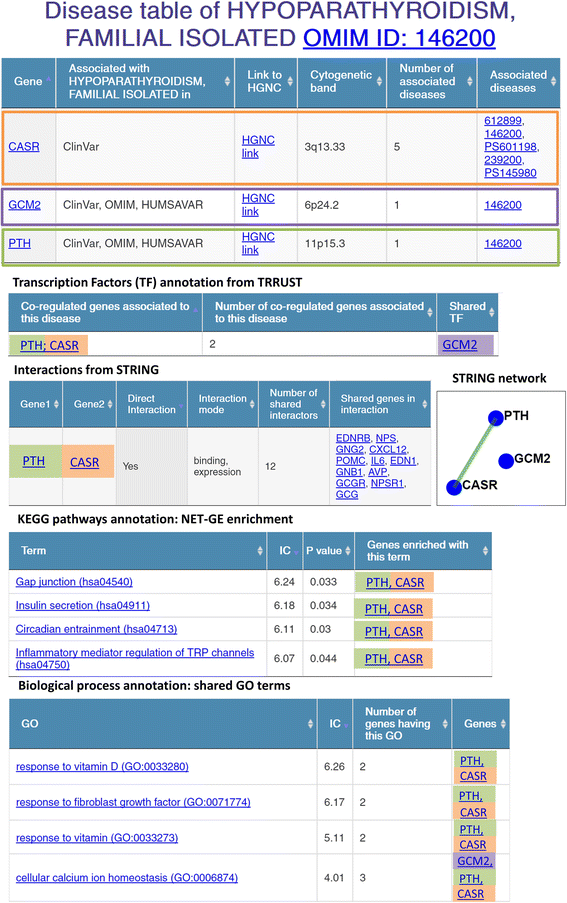
Results: We present eDGAR, a database collecting and organizing the data on gene/disease associations as derived from OMIM, Humsavar and ClinVar. For each disease-associated gene, eDGAR collects information on its annotation. Specifically, for lists of genes, eDGAR provides information on: i) interactions retrieved from PDB, BIOGRID and STRING; ii) co-occurrence in stable and functional structural complexes; iii) shared Gene Ontology annotations; iv) shared KEGG and REACTOME pathways; v) enriched functional annotations computed with NET-GE; vi) regulatory interactions derived from TRRUST; vii) localization on chromosomes and/or co-localisation in neighboring loci. The present release of eDGAR includes 2672 diseases, related to 3658 different genes, for a total number of 5729 gene-disease associations. 71% of the genes are linked to 621 multigenic diseases and eDGAR highlights their common GO terms, KEGG/REACTOME pathways, physical and regulatory interactions. eDGAR includes a network based enrichment method for detecting statistically significant functional terms associated to groups of genes.
Conclusions: eDGAR offers a resource to analyze disease-gene associations. In multigenic diseases genes can share physical interactions and/or co-occurrence in the same functional processes. eDGAR is freely available at: edgar.biocomp.unibo.it.
Keywords: Functional enrichment; Gene/disease relationship; Protein functional annotation; Protein-protein interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors declare that they used only public data.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Landrum MJ, Lee JM, Benson M, Brown G, Chao C, Chitipiralla S, Gu B, Hart J, Hoffman D, Hoover J, Jang W, Katz K, Ovetsky M, Riley G, Sethi A, Tully R, Villamarin-Salomon R, Rubinstein W, Maglott DR. ClinVar: public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(D1):D862–D868. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1222. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stenson PD, Ball EV, Mort M, Phillips AD, Shaw K, Cooper DN. The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) and its exploitation in the fields of personalized genomics and molecular evolution. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2012;39:1.13:1.13.1–1.13.20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

