Four Challenges That Global Health Networks Face
- PMID: 28812801
- PMCID: PMC5384980
- DOI: 10.15171/ijhpm.2017.14
Four Challenges That Global Health Networks Face
Abstract
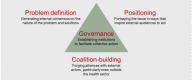
Global health networks, webs of individuals and organizations with a shared concern for a particular condition, have proliferated over the past quarter century. They differ in their effectiveness, a factor that may help explain why resource allocations vary across health conditions and do not correspond closely with disease burden. Drawing on findings from recently concluded studies of eight global health networks-addressing alcohol harm, early childhood development (ECD), maternal mortality, neonatal mortality, pneumonia, surgically-treatable conditions, tobacco use, and tuberculosis-I identify four challenges that networks face in generating attention and resources for the conditions that concern them. The first is problem definition: generating consensus on what the problem is and how it should be addressed. The second is positioning: portraying the issue in ways that inspire external audiences to act. The third is coalition-building: forging alliances with these external actors, particularly ones outside the health sector. The fourth is governance: establishing institutions to facilitate collective action. Research indicates that global health networks that effectively tackle these challenges are more likely to garner support to address the conditions that concern them. In addition to the effectiveness of networks, I also consider their legitimacy, identifying reasons both to affirm and to question their right to exert power.
Keywords: Coalition-Building; Effectiveness; Framing; Global Health Networks; Governance.
© 2017 The Author(s); Published by Kerman University of Medical Sciences. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Comment in
-
Global Alcohol Harm Network: Struggling or Emerging? A Response to Shiffman.Int J Health Policy Manag. 2017 Aug 1;6(8):487-488. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2017.31. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2017. PMID: 28812850 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Polycentrism in Global Health Governance Scholarship Comment on "Four Challenges That Global Health Networks Face".Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018 Jan 1;7(1):78-80. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2017.64. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018. PMID: 29325406 Free PMC article.
-
The Magic Pudding Comment on "Four Challenges That Global Health Networks Face".Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018 Feb 1;7(2):192-194. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2017.76. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018. PMID: 29524945 Free PMC article.
-
State Support: A Prerequisite for Global Health Network Effectiveness Comment on "Four Challenges that Global Health Networks Face".Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018 Mar 1;7(3):275-277. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2017.86. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018. PMID: 29524958 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges Facing Global Health Networks: The NCD Alliance Experience Comment on "Four Challenges that Global Health Networks Face".Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018 Mar 1;7(3):282-285. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2017.93. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018. PMID: 29524960 Free PMC article.
-
Additional Insights Into Problem Definition and Positioning From Social Science Comment on "Four Challenges That Global Health Networks Face".Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018 Apr 1;7(4):362-364. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2017.108. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018. PMID: 29626407 Free PMC article.
-
Agency, Structure and the Power of Global Health Networks.Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018 Oct 1;7(10):879-884. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2018.71. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018. PMID: 30316239 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous