Pharmacotherapy for hypertension in adults aged 18 to 59 years
- PMID: 28813123
- PMCID: PMC6483466
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008276.pub2
Pharmacotherapy for hypertension in adults aged 18 to 59 years
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is an important risk factor for adverse cardiovascular events including stroke, myocardial infarction, heart failure and renal failure. The main goal of treatment is to reduce these events. Systematic reviews have shown proven benefit of antihypertensive drug therapy in reducing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality but most of the evidence is in people 60 years of age and older. We wanted to know what the effects of therapy are in people 18 to 59 years of age.
Objectives: To quantify antihypertensive drug effects on all-cause mortality in adults aged 18 to 59 years with mild to moderate primary hypertension. To quantify effects on cardiovascular mortality plus morbidity (including cerebrovascular and coronary heart disease mortality plus morbidity), withdrawal due adverse events and estimate magnitude of systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) lowering at one year.
Search methods: The Cochrane Hypertension Information Specialist searched the following databases for randomized controlled trials up to January 2017: the Cochrane Hypertension Specialised Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE (from 1946), Embase (from 1974), the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and ClinicalTrials.gov. We contacted authors of relevant papers regarding further published and unpublished work.
Selection criteria: Randomized trials of at least one year' duration comparing antihypertensive pharmacotherapy with a placebo or no treatment in adults aged 18 to 59 years with mild to moderate primary hypertension defined as SBP 140 mmHg or greater or DBP 90 mmHg or greater at baseline, or both.
Data collection and analysis: The outcomes assessed were all-cause mortality, total cardiovascular (CVS) mortality plus morbidity, withdrawals due to adverse events, and decrease in SBP and DBP. For dichotomous outcomes, we used risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) and a fixed-effect model to combine outcomes across trials. For continuous outcomes, we used mean difference (MD) with 95% CI and a random-effects model as there was significant heterogeneity.
Main results: The population in the seven included studies (17,327 participants) were predominantly healthy adults with mild to moderate primary hypertension. The Medical Research Council Trial of Mild Hypertension contributed 14,541 (84%) of total randomized participants, with mean age of 50 years and mean baseline blood pressure of 160/98 mmHg and a mean duration of follow-up of five years. Treatments used in this study were bendrofluazide 10 mg daily or propranolol 80 mg to 240 mg daily with addition of methyldopa if required. The risk of bias in the studies was high or unclear for a number of domains and led us to downgrade the quality of evidence for all outcomes.Based on five studies, antihypertensive drug therapy as compared to placebo or untreated control may have little or no effect on all-cause mortality (2.4% with control vs 2.3% with treatment; low quality evidence; RR 0.94, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.13). Based on 4 studies, the effects on coronary heart disease were uncertain due to low quality evidence (RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.19). Low quality evidence from six studies showed that drug therapy may reduce total cardiovascular mortality and morbidity from 4.1% to 3.2% over five years (RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.91) due to reduction in cerebrovascular mortality and morbidity (1.3% with control vs 0.6% with treatment; RR 0.46, 95% CI 0.34 to 0.64). Very low quality evidence from three studies showed that withdrawals due to adverse events were higher with drug therapy from 0.7% to 3.0% (RR 4.82, 95% CI 1.67 to 13.92). The effects on blood pressure varied between the studies and we are uncertain as to how much of a difference treatment makes on average.
Authors' conclusions: Antihypertensive drugs used to treat predominantly healthy adults aged 18 to 59 years with mild to moderate primary hypertension have a small absolute effect to reduce cardiovascular mortality and morbidity primarily due to reduction in cerebrovascular mortality and morbidity. All-cause mortality and coronary heart disease were not reduced. There is lack of good evidence on withdrawal due to adverse events. Future trials in this age group should be at least 10 years in duration and should compare different first-line drug classes and strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
VM: none.
FG: none.
LP: none.
DS: none.
JMW: none.
Figures

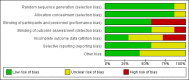
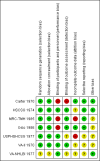



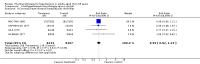



Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008276
References
References to studies included in this review
Carter 1970 {published data only}
-
- Carter AB. Hypotensive therapy in stroke survivors. Lancet 1970;1:485‐89. - PubMed
HSCSG 1974 {published data only}
-
- Hypertension‐Stroke Cooperative Study Group. Effect of antihypertensive treatment on stroke recurrence. JAMA 1974;229:409‐18. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
MRC‐TMH 1985 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Adverse reactions to bendrofluazide and propranolol for the treatment of mild hypertension. Report of Medical Research Council Working Party on Mild to Moderate Hypertension. Lancet 1981;2(8246):539‐43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Comparison of the antihypertensive efficacy and adverse reactions of two doses of bendrofluazide and hydrochlorothiazide and the effect of potassium supplementation on the hypotensive action of bendrofluazide: sub‐studies of the Medical Research Council's trials of treatment of mild hypertension: Medical Research Council Working Party. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1987;27(4):271‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Comparison of the antihypertensive efficacy and adverse reactions to two doses of bendrofluazide and hydrochlorothiazide and the effect of potassium supplementation on the hypotensive action of bendrofluazide: substudies of the Medical Research Council's trials of treatment of hypertension: Medical Research Council Working Party. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1987;27(4):271‐7. [MEDLINE: ; CRSREF: 3042232] - PubMed
Oslo 1986 {published data only}
-
- Helgeland A. Treatment of mild hypertension: a five year controlled drug trial. The OSLO study. American Journal of Medicine 1980;69:725‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Helgeland A, Baksaas IA, Leren P. Mild hypertension ‐ early drug treatment or follow‐up only? the Oslo study. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1979;626:34‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Helgeland A, Hjermann I, Holme I, Liren P. Serum triglycerides and serum uric acid in untreated and thiazide‐treated patients with mild hypertension. American Journal of Medicine 1978;64:34‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Helgeland A, Leren P. Oslo study: treatment of mild hypertension. Nephron 1987;47(Suppl 1):108‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Helgeland A, Leren P, Foss OP, Hjermann I, Holme I, Lund‐Larsen PG. Serum glucose levels during long‐term observation of treated and untreated men with mild hypertension. American Journal of Medicine 1984;76:802‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
USPHSHCSG 1977 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Morbidity and mortality in mild essential hypertension. Circulation Research 1972;30/31(Suppl II):110‐20. - PubMed
-
- Smith WM, Johnson WP, Bromer L. Intervention trial in mild hypertension, U.S. Public Health Service Hospitals Cooperative Study Group. Miami (FL): Symposia Specialists: In Epidemiology and Control of Hypertension, 1975.
-
- US Public Health Service Hospital Cooperative Study Group (USPHSHCSG). Treatment of mild hypertension. Results of a ten‐year intervention trial. Circulation Research 1977;40(Suppl 1):98‐105. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
VA‐II 1970 {published data only}
-
- Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. Effects of treatment on morbidity in hypertension II. Results in patients with diastolic blood pressure averaging 90 through 114 mm Hg. JAMA 1970;213:1143‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. Effects of treatment on morbidity in hypertension: influence of age, diastolic pressure, and prior cardiovascular disease: further analysis of side effects. Circulation 1972;45:991‐1004. - PubMed
VA‐NHLBI 1977 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Evaluation of drug treatment in mild hypertension: VA‐NHLBI feasibility trial. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1978;304:267‐88. [MEDLINE: ; CRSREF: 3042309] - PubMed
-
- Perry HM Jr. Treatment of mild hypertension. Preliminary results of a two year feasibility trial. Circulation Research 1977;40 Suppl:1180‐7. [MEDLINE: ; CRSREF: 3042310] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
ADVANCE 2007 {published data only}
-
- The ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Effects of a fixed combination of perindopril and indapamide on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the ADVANCE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007;370:829‐40. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61303-8] - DOI - PubMed
ALLHAT 1996 {published data only}
-
- ALLHAT Group. Diuretic versus alpha‐blocker as first‐step antihypertensive therapy: final results from the Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Hypertension 2003;42:239‐46. - PubMed
-
- Davis BR, Cutler JA, Gordon DJ, Furberg CD, Wright JT Jr, Cushman WC, et al. for the ALLHAT Research Group. Rationale and design for the Antihypertensive and Lipid Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). American Journal of Hypertension 1996;9:342‐60. - PubMed
Anon 1973 {published data only}
ATTMH 1984 {published data only}
-
- Abernethy JD. The Australian Therapeutic Trial in Mild Hypertension. Hypertension 1984;6(5):774‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Australian National Blood Pressure Management Committee. The Australian Therapeutic Trial in Mild Hypertension. Lancet 1980;1:1261‐7. - PubMed
-
- The Management Committee. Treatment of mild hypertension in the elderly. A study initiated and administered by the National Heart Foundation of Australia. Medical Journal of Australia 1981;2:398‐402. - PubMed
Berglund 1981 {published data only}
-
- Berglund G, Andersson O. Beta‐blockers or diuretics in hypertension? A six year follow up of blood pressure and metabolic side effects. Lancet 1981;I:744‐7. - PubMed
CASTEL 1994 {published data only}
-
- Casiglia E, Spolaore P, Mazza A, Ginocchio G, Colangeli G, Onesto C, et al. Effect of two different therapeutic approaches on total and cardiovascular mortality in a Cardiovascular Study in the Elderly (CASTEL). Japanese Heart Journal 1994;35(5):589‐600. - PubMed
-
- Casiglia E, Spolaore P, Mormino P, Maschio O, Colangeli G, Celegon L. The CASTEL project (CArdiovascular STudy in the ELderly): protocol, study design, and preliminary results of the initial survey. Cardiologia 1991;36:569‐76. - PubMed
Coope 1986 {published data only}
Dutch TIA 1993 {published data only}
-
- Dutch TIA Trial Study Group. Trial of secondary prevention with atenolol after transient ischemic attack or non‐disabling ischemic stroke. Stroke 1993;24:543‐8. - PubMed
EWPHBPE 1988 {published data only}
-
- European Working Party on High Blood Pressure in the Elderly (EWPHE). An international trial of antihypertensive therapy in elderly patients. Objectives, protocol and organization. Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie 1985;275:300‐34. - PubMed
-
- O'Malley KO, McCormack P, O'Brien ET. Isolated systolic hypertension: data from the European Working Party on High Blood Pressure in the Elderly. Journal of Hypertension 1988;6(Suppl 1):S105‐8. - PubMed
Fuchs 2011 {published data only}
GENERIC 2010 {published data only}
-
- Punzi HA, Lewin AJ, Lukic T, Goodin T, Chen W. Efficacy and safety of nebivolol monotherapy in Hispanics with stage I‐II hypertension (Abstract). Journal of Clinical Hypertension 2010;12:536. - PubMed
GLANT 1995 {published data only}
-
- Study Group on Long‐term Antihypertensive Therapy. A 12‐month comparison of ACE inhibitor and CA antagonist therapy in mild to moderate essential hypertension ‐ the GLANT Study. Hypertension Research 1995;18:235‐44. - PubMed
HANE 1997 {published data only}
HAPPHY 1987 {published data only}
-
- Wilhelmsen L, Berglund G, Elmfeldt D, Fitzsimons T, Holzgreve H, Hosie J, et al. Beta‐blockers versus diuretics in hypertensive men: main results from the HAPPHY trial. Journal of Hypertension 1987;5(5):561‐72. - PubMed
HDFP 1982 {published data only}
-
- Curb JD, Borhani NO, Schnaper H, Kass E, Entwisle G, Williams W, et al. Detection and treatment of hypertension in older individuals. American Journal of Epidemiology 1985;121(3):371‐6. - PubMed
-
- Hypertension Detection and Follow‐up Program Cooperative Group. Five‐year findings of the Hypertension Detection and Follow‐up Program: reduction in mortality in persons with high blood pressure, including mild hypertension. JAMA 1979;242:2562‐71. - PubMed
HOPE HYP 2000 {published data only}
-
- Yusuf S, Sleight P, Pogue J, Bosch J, Davies R, Dagenais G. Effects of an angiotensin‐converting‐enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high‐risk patients. The Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Outcomes Study Investigators. New England Journal of Medicine 2000;342(3):145‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
HOT 1995 {published data only}
-
- Hansson L, Zanchetti A. The Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) Study: 12‐month data on blood pressure and tolerability. With special reference to age and gender. Blood Pressure 1995;4:313‐9. - PubMed
HYVET 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bulpitt CJ, Beckett NS, Cooke J, Dumiktrascu DL, Gil‐Extremera B, Nachev C, et al. Results of the pilot study for the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial. Journal of Hypertension 2003;21:2409‐17. - PubMed
HYVET 2008 {published data only}
-
- Beckett NS, Peters R, Fletcher AE, Staessen JA, Liu L, Dumitrascu D, et al. Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358(18):1887‐98. - PubMed
-
- Peters R, Beckett N, Forette F, Tuomilehto J, Clarke R, Ritchie C, et al. Incident dementia and blood pressure lowering in the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial cognitive function assessment (HYVET‐COG): a double‐blind, placebo controlled trial. Lancet Neurology 2008;7(8):683‐9. - PubMed
IDM 2001 {published data only}
-
- Parving HH, Lehnert H, Brochner‐Mortensen J, Gomis R, Andersen S, Arner P. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;345:870‐8. - PubMed
INSIGHT 1996 {published data only}
-
- Brown MJ, Castaigne A, Ruilope LM, Mancia G, Rosenthal T, Leeuw PW, et al. INSIGHT: International Nifedipine GITS study: intervention as a goal in hypertension treatment. Journal of Human Hypertension 1996;10(Suppl 13):S157‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Brown MJ, Castaigne A, Leeuw PW, Mancia G, Rosenthal T, Ruilope LM. Study population and treatment titration in the International Nifedepine GITS study: intervention as a goal in hypertension treatment (INSIGHT). Journal of Hypertension 1998;16:2113‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Brown MJ, Palmer CR, Castaigne A, Leeuw PW, Mancia G, Rosenthal T, et al. Morbidity and mortality in patients randomised to double‐blind treatment with long‐acting calcium‐channel blocker or diuretic in the International Nifedipine GITS study. Lancet 2000;356:366‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
IPPPSH 1985 {published data only}
-
- IPPPSH Collaborative Group. Cardiovascular risk and risk factors in a randomized trial of treatment based on the beta‐blocker oxprenolol: the International Prospective Primary Prevention Study in Hypertension (IPPPSH). Journal of Hypertension 1985;3(4):379‐92. - PubMed
Jikei 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mochizuki S, Dahlof B, Shimizu M, Ikewaki K, Yoshikawa M, Taniguchi I, et al. Valsartan in a Japanese population with hypertension and other cardiovascular disease (Jikei Heart Study): a randomised, open‐label, blinded end point morbidity‐mortality study. Lancet 2007;369:1431‐9. - PubMed
Kuramoto 1981 {published data only}
-
- Kuramoto K, Matsushita S, Kuwajima T, Murakami M. Prospective study on the treatment of mild hypertension in the aged. Japanese Heart Journal 1981;22(1):75‐85. - PubMed
Kuramoto 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kuramoto K. Treatment of the elderly hypertensives in Japan: National Intervention Cooperative Study in Elderly Hypertensives. The National Intervention Cooperative Study Group. Journal of Hypertension 1994;12(6):S35‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lewis 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin‐receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;345:851‐60. - PubMed
MAPHY 1988 {published data only}
-
- Wikstrand J, Warnold I, Olsson G, Tuomilehto J, Elmfeldt D, Berglund G. Primary prevention with metoprolol in patients with hypertension. Mortality results from the MAPHY study. JAMA 1988;259(13):1976‐82. - PubMed
Materson 1993 {published data only}
-
- Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Cushman WC, Massie BM, Freis ED, Kochar MS, et al. Single‐drug therapy for hypertension in men: a comparison of six antihypertensive agents with placebo. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;328(13):914‐21. - PubMed
-
- Materson BJ. Reda DJ, Cushman WC. Department of Veterans Affairs single‐drug therapy of hypertension study. Revised figures and new data. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. American Journal of Hypertension 1995;8(2):189‐92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
MIDAS 1996 {published data only}
-
- Borhani NO, Mercuri M, Borhani PA, Buckalew VM, Canossa‐Terris M, Carr AA, et al. Final outcome results of the Multicenter Isradipine Diuretic Atherosclerosis Study (MIDAS). JAMA 1996;276(10):785‐91. - PubMed
Morgan 1980 {published data only}
-
- Morgan TO, Adams WR, Hodgson M, Gibberd RW. Failure of therapy to improve prognosis in elderly males with hypertension. Medical Journal of Australia 1980;2(1):27‐31. - PubMed
MRCO 1992 {published data only}
NORDIL 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hansson L, Hedner T, Lund‐Johansen P, Kjeldsen SE, Lindholm LH, Syvertsen JO, et al. Randomised trial of effects of calcium antagonists compared with diuretics and beta‐blockers on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertension: the Nordic Diltiazem (NORDIL) study. Lancet 2000;356(9227):359‐65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
PATS 1995 {published data only}
-
- PATS Collaborating Group. Post‐stroke antihypertensive treatment study. A preliminary result. Chinese Medical Journal 1995;108(9):710‐7. - PubMed
PROGRESS 2001 {published data only}
-
- PROGRESS Collaborative Group. Randomised trial of a perindopril‐based blood‐pressure‐lowering regimen among 6105 individuals with previous stroke or transient ischemic attack. Lancet 2001;358:1033‐41. - PubMed
QUIET 2001 {published data only}
-
- Pitt B, O'Neill B, Feldman R, Ferrari R, Schwartz L, Judra H, et al. The QUinapril Ischemic Event Trial (QUIET): evaluation of chronic ACE inhibitor therapy in patients with ischemic heart disease and preserved left ventricular function. American Journal of Cardiology 2001;87:1058‐63. - PubMed
SCAT 2000 {published data only}
-
- Teo KK, Burton JR, Buller CE, Plante S, Catellier D, Tymchak W, et al. Long‐term effects of cholesterol lowering and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition on coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation 2000;102:1748‐54. - PubMed
Schmieder 2009 {published data only}
-
- Schmieder RE, Philipp T, Guerediaga J, Gorostidi M, Smith B, Weissbach N, et al. Long‐term antihypertensive efficacy and safety of the oral direct renin Inhibitor aliskiren. A 12‐month randomized, double‐blind comparator trial with hydrochlorothiazide. Circulation 2009;119(3):417‐25. [DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.750745] - DOI - PubMed
SCOPE 2003 {published data only}
SHELL 1994 {published data only}
-
- Malacco E, Gnemmi AE, Romagnoli A, Coppini A. Systolic hypertension in the elderly: long‐term lacidipine treatment. Objective, protocol, and organization. SHELL Study Group. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1994;23(5):S6206. - PubMed
SHEP 1991 {published data only}
-
- SHEP Cooperative Research Group. Prevention of stroke by antihypertensive drug treatment in older persons with isolated systolic hypertension: final results of the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP). JAMA 1991;265(24):3255‐64. - PubMed
-
- SHEP Cooperative Research Group. Rationale and design of a randomized clinical trial on prevention of stroke in isolated systolic hypertension. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1988;41(12):1197‐208. - PubMed
SHEP ‐ Pilot 1985 {published data only}
-
- Perry HM, Smith WM, McDonald RH, Black D, Cutler JA, Furberg CD, et al. Morbidity and mortality in the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP) Pilot Study. Stroke 1989;20(1):4‐13. - PubMed
Sprackling 1981 {published data only}
STONE 1996 {published data only}
-
- Gong L, Zwang W, Zhu Y, Hamet P. Shanghai Trial of Nifedipine in the Elderly (STONE) study. Journal of Hypertension 1996;14:1237‐46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
STOP 1991 {published data only}
-
- Dahlöf B, Lindholm LH, Hansson L, Scherstén B, Ekbom T, Wester PO. Morbidity and mortality in the Swedish Trial in Old Patients with Hypertension (STOPHypertension). Lancet 1991;338:1281‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
STOP‐2 1993 {published data only}
-
- Dahlöf B, Hansson L, Lindholm LH, Scherstén B, Wester PO, Ekbom T. STOP‐Hypertension‐2: a prospective intervention trial of "newer" versus "older" treatment alternatives in old patients with hypertension. Blood Pressure 1993;2:136‐41. - PubMed
Strandberg 1991 {published data only}
-
- Strandberg TE, Salomaa VV, Naukkarinen VA, Vanhanen HT, Sarna SJ, Miettinen TA. Long‐term mortality after 5‐year multifactorial primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases in middle‐aged men. JAMA 1991;266(9):1255‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Syst China 1993 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Systolic hypertension in the elderly: Chinese trial (Syst‐China). Interim report. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing za Zhi 1992;20(5):270‐5, 323. - PubMed
Syst‐Eur 1991 {published data only}
-
- Amery A, Birkenhager W, Bulpitt CJ, Clément D, Leeuw P, Dollery CT, et al. Syst‐Eur: a multicenter trial on the treatment of isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly; objectives, protocol and organisation. Aging 1991;3:287‐302. - PubMed
TEST 1995 {published data only}
-
- Eriksson S, Olofsson BO, Wesley PO, for the TEST study group. Atenolol for secondary prevention after stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases (Basel, Switzerland) 1995;5:21‐5.
TOMHS 1995 {published data only}
-
- Elmer PJ, Grimm R, Laing B, Grandits G, Svedsen K, Heel N, et al. Lifestyle intervention: results of the Treatment of Mild Hypertension Study (TOMHS). Preventive Medicine 1995;24:378‐88. - PubMed
UKPDS 1998 {published data only}
VA Coop 1960 {published data only}
-
- Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. A double‐blind control study of antihypertensive agents. I. Comparative effect of reserpine, reserpine and hydralazine, and three ganglionic blocking agents, clorisondamine, mecamylamine, and pentolinium tartrate. Archives of Internal Medicine 1960;106:133‐48. - PubMed
VACS 1982 {published data only}
-
- Veterans Administrative Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. Comparison of propranolol and hydrochlorothiazide for the initial treatment of hypertension. II Results of long term therapy. JAMA 1982;248:2004‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
VA‐I 1962 {published data only}
-
- Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. A double‐blind control study of antihypertensive agents. III. Chlorothiazide alone and in combination with other agents: preliminary results. Archives of Internal Medicine 1962;110:230‐5.
VHAS 1997 {published data only}
-
- Agabiti RE, Dal Palu D, Leonetti G, Magnani G, Pessina A, Zanchetti A. Clinical results of the verapamil in hypertension and atherosclerosis study. Journal of Hypertension 1997;15:1337‐44. - PubMed
White 1995 {published data only}
-
- White WB, Stimpel M. Long‐term safety and efficacy of moexipril alone and in combination with hydrochlorothiazide in elderly patients with hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 1995;9(11):879‐84. - PubMed
Wolff 1966 {published data only}
-
- Wolff FW, Lindeman RD. Effects of treatment in hypertension. Results of a controlled study. Journal of Chronic Diseases 1966;19:227‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
BBLTTC 2005
-
- Turnbull F, Neal B, Albert C, Chalmers J, Chapman N, Cutler J, et al. Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists' Collaboration. Effects of different blood pressure‐lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events in individuals with and without diabetes mellitus: results of prospectively designed overviews of randomized trials. Archives of Internal Medicine 2005;165(12):1410‐9. - PubMed
Boissel 2005
-
- Boissel JP, Gueyffier F, Boutitie F, Pocock S, Fagard R. Apparent effect on blood pressure is only partly responsible for the risk reduction due to antihypertensive treatments. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology 2005;19:579‐84. - PubMed
BPLTTC 2008
-
- Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists' Collaboration, Turnbull F, Neal B, Ninomiya T, Algert C, Arima H, Barzi F, et al. Effects of different regimens to lower blood pressure on major cardiovascular events in older and younger adults: meta‐analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2008;336(7653):1121‐3. - PMC - PubMed
Collins 1990
-
- Collins R, Peto R, MacMahon S, Hebert P, Fiebach NH, Eberlein KA, et al. Blood pressure, stroke, and coronary heart disease ‐ Part 2, short‐term reductions in blood pressure: overview of randomised drug trials in their epidemiological context. Lancet 1990;335:827‐38. - PubMed
Duarte 2010
Frishman 2005
-
- Frishman WH, Cheng‐Lai A, Nawarskas J. Current Cardiovascular Drugs. 4th Edition. Philadelphia, PA 19106: Springer Science & Business Media, 2005.
GRADEpro
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editors. GRADE handbook for grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. The GRADE Working Group, 2013. Available from guidelinedevelopment.org/handbook, Updated October 2013.
Gueyffier 1995
-
- Gueyffier F, Boutitie F, Boissel JP, Coope J, Cutler J, Ekbom T, et al. INDANA: a meta‐analysis on individual patient data in hypertension. Protocol and preliminary results. Therapie 1995;50:353‐62. - PubMed
Gueyffier 1996
-
- Gueyffier F, Froment A, Gouton M. New meta‐analysis of treatment trials of hypertension: improving the estimate of therapeutic benefit. Journal of Human Hypertension 1996;10:1‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gueyffier 1999
-
- Gueyffier F, Bulpitt C, Boissel JP, Schron E, Ekbom T, Fagard R, et al. for the INDANA Group. Antihypertensive drugs in very old people: a subgroup meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet 1999;353:793‐6. - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hughes 2004
-
- Hughes AD. How do thiazide and thiazide‐like diuretics lower blood pressure?". Journal of the Renin‐Angiotensin‐Aldosterone System 2004;5(4):155‐60. - PubMed
Insua 1994
-
- Insua JT, Sacks HS, Lau TS, Lau J, Reitman D, Pagano D, et al. Drug treatment of hypertension in the elderly: a meta‐analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 1994;121:355‐62. - PubMed
James 2014
-
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison‐Himmelfarb C, Handler J, et al. Evidence‐based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014;311(5):507‐20. - PubMed
Kang 2004
-
- Kang S, Wu FY, An N, Ren M. A systematic review and meta‐analysis of the efficacy and safety of a fixed low‐dose perindopril‐indapamide combination as first‐line treatment of hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 2004;26(2):257‐70. - PubMed
Kearney 2005
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005;365:217‐23. - PubMed
Kızılırmak 2017
-
- Kızılırmak P, Uresin Y, Ozdemir O, Kilickiran B, Tokgözoğlu L, Öngen Z. Renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system blockers and cardiovascular outcomes: a meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials [Renin‐anjiyotensin‐aldosteron sistemi blokerleri ve kardiyovasküler sonuçları: Randomize klinik çalışmaların meta‐analizi]. Turk Kardiyoloji Dernegi Arsivi 2017;45(1):49‐66. - PubMed
Law 2009
Longo 2012
-
- Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principals of Internal Medicine. Vol. 2, New York (NY): McGraw‐Hill, 2012. [ISBN 978‐0‐07‐174887‐2]
MacMahon 1993
-
- MacMahon S, Rogers A. The effects of blood pressure reduction in older patients: an overview of five randomized controlled trials in elderly hypertensives. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension 1993;15(6):967‐78. - PubMed
Mancia 2013
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redón J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, et al. Task Force Members, 2013. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal 2013;34:2159‐219. - PubMed
Mulrow 1994
-
- Mulrow CD, Cornell JA, Herrera CR, Kadri A, Farnett L, Aguilar C. Hypertension in the elderly: Implications and generalizability of randomized trials. JAMA 1994;272:1932‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mulrow 1998
Musini 2009
NICE 2016
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Treating high blood pressure with lifestyle changes, August 2011, updated November 2016. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg127/ifp/chapter/treating‐high‐blood‐pressure‐... (accessed prior to 28 July 2017).
Nikolaus 2000
-
- Nikolaus T, Sommer N, Becker C. Treatment of arterial hypertension with diuretics, beta‐ and calcium channel blockers in old patients. Zeitschrift fur Gerontologie und Geriatrie 2000;33:427‐32. - PubMed
Parsons 2016
-
- Parsons C, Murad MH, Andersen S, Mookadam F, Labonte H. The effect of antihypertensive treatment on the incidence of stroke and cognitive decline in the elderly: a meta‐analysis. Future Cardiology 2016;12(2):237‐48. - PubMed
Pearce 1995
-
- Pearce KA, Furberg CD, Rushing J. Does antihypertensive treatment of the elderly prevent cardiovascular events or prolong life? A meta‐analysis of hypertension treatment trials. Archives of Family Medicine 1995;4:943‐50. - PubMed
Prospective Studies Collaboration 2002
-
- Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R. Age‐specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta‐analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002;360(9349):1903‐13. - PubMed
Psaty 1997
-
- Psaty BM, Smith NL, Siscovick DS, Koepsell TD, Weiss NS, Heckbert SR, et al. Health outcomes associated with antihypertensive therapies used as first‐line agents. A systematic review and meta‐analysis. JAMA 1997;277(9):739‐45. - PubMed
Psaty 2003
-
- Psaty BM, Lumley T, Furberg CD, Schellenbaum G, Pahor M, Alderman MH, et al. Health outcomes associated with various antihypertensive therapies used as first‐line agents: a network meta‐analysis. JAMA 2003;289:2534‐44. - PubMed
Quan 1999
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager. Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Sundström 2015
-
- Sundström J, Arima H, Jackson R, Turnbull F, Rahimi K, Chalmers J, et al. Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists' Collaboration. Effects of blood pressure reduction in mild hypertension. A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2015;162:184‐91. - PubMed
Tan 2016
-
- Tan XY, Hu JB. ACEIs/ARBs for the prevention of type 2 diabetes in patients with cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2016;9(5):7624‐37.
Thijs 1992
-
- Thijs L, Fagard R, Lijnen P, Staessen J, Hoof R, Amery A. A meta‐analysis of outcome trials in elderly hypertensives. Journal of Hypertension 1992;10:1103‐9. - PubMed
Thomopoulos 2014
-
- Thomopoulos C, Parati G, Zanchetti A. Effects of blood pressure lowering on outcome incidence in hypertension. 1. Overview, meta‐analyses, and meta‐regression analyses of randomized trials. Journal of Hypertension 2014;32(12):2285‐95. - PubMed
Thomopoulos 2016
-
- Thomopoulos C, Parati G, Zanchetti A. Effects of blood pressure‐lowering treatment. 6. Prevention of heart failure and new‐onset heart failure ‐ meta‐analyses of randomized trials. Journal of Hypertension 2016;34(3):373‐84. - PubMed
Turnbull 2003
-
- Turnbull F, Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists' Collaboration. Effects of different blood‐pressure‐lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events: results of prospectively‐designed overviews of randomised trials. Lancet 2003;362:1527‐35. - PubMed
Weber 2014
-
- Weber MA, Schiffrin EL, White WB, Mann S, Lindholm LH, Kenerson JG, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypertension in the community. A statement by the American Society of Hypertension and the International Society of Hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 2014;32(1):3‐15. - PubMed
WHO 2003
-
- World Health Organization, International Society of Hypertension Writing Group. 2003 World Health Organization/International Society of Hypertension (ISH) statement on management of hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 2003;21:1983‐92. - PubMed
Wiysonge 2017
Wright 2009
Zanchetti 2015
-
- Zanchetti A, Thomopoulos C, Parati G. Randomized controlled trials of blood pressure lowering in hypertension: a critical reappraisal. Circulation Research 2015;116(6):1058‐73. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Musini 2010
-
- Musini VM, Tejani AM, Labeit AM, Salzwedel DM, Wright JM. Pharmacotherapy for hypertension in non‐elderly adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008276] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

