CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity
- PMID: 28813415
- PMCID: PMC5570667
- DOI: 10.1038/nature23465
CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity
Abstract
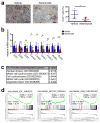
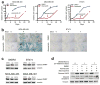
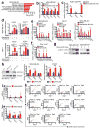
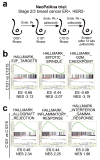
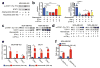
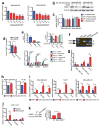
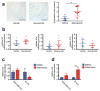
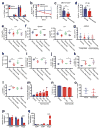
Cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) are fundamental drivers of the cell cycle and are required for the initiation and progression of various malignancies. Pharmacological inhibitors of CDK4/6 have shown significant activity against several solid tumours. Their primary mechanism of action is thought to be the inhibition of phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma tumour suppressor, inducing G1 cell cycle arrest in tumour cells. Here we use mouse models of breast carcinoma and other solid tumours to show that selective CDK4/6 inhibitors not only induce tumour cell cycle arrest, but also promote anti-tumour immunity. We confirm this phenomenon through transcriptomic analysis of serial biopsies from a clinical trial of CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment for breast cancer. The enhanced anti-tumour immune response has two underpinnings. First, CDK4/6 inhibitors activate tumour cell expression of endogenous retroviral elements, thus increasing intracellular levels of double-stranded RNA. This in turn stimulates production of type III interferons and hence enhances tumour antigen presentation. Second, CDK4/6 inhibitors markedly suppress the proliferation of regulatory T cells. Mechanistically, the effects of CDK4/6 inhibitors both on tumour cells and on regulatory T cells are associated with reduced activity of the E2F target, DNA methyltransferase 1. Ultimately, these events promote cytotoxic T-cell-mediated clearance of tumour cells, which is further enhanced by the addition of immune checkpoint blockade. Our findings indicate that CDK4/6 inhibitors increase tumour immunogenicity and provide a rationale for new combination regimens comprising CDK4/6 inhibitors and immunotherapies as anti-cancer treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Shom Goel has served as a paid scientific advisor to Eli Lilly, and conducts laboratory research funded by Eli Lilly. Eli Lilly did not fund the present study. Matthew Ellis has performed ad hoc consulting for Novartis, Pfizer, and AstraZeneca, receives royalties for PAM50-based diagnostics including Prosigna, and holds stock in Bioclassifier LLC for PAM50-based diagnostics.
Figures





Comment in
-
Tumour immunology: Cell cycle inhibitors boost tumour immunogenicity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Aug 30;17(9):529. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.104. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28853445 No abstract available.
-
CDK4/6 Inhibitors Induce Antitumor Immunity.Cancer Discov. 2017 Oct;7(10):1052. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2017-122. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Cancer Discov. 2017. PMID: 28864481
-
Cancer immunotherapy: Cell cycle inhibitors boost tumour immunogenicity.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017 Sep 29;16(10):679. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.199. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28959946 No abstract available.
References
-
- Patnaik A, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Abemaciclib, an Inhibitor of CDK4 and CDK6, for Patients with Breast Cancer, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, and Other Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:740–753. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0095. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1501–1512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

