CMTM6 maintains the expression of PD-L1 and regulates anti-tumour immunity
- PMID: 28813417
- PMCID: PMC5706633
- DOI: 10.1038/nature23643
CMTM6 maintains the expression of PD-L1 and regulates anti-tumour immunity
Abstract
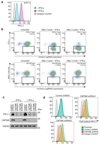
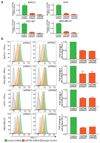
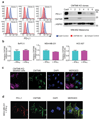
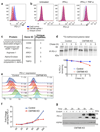
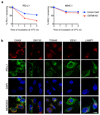
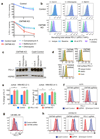
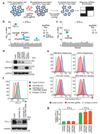
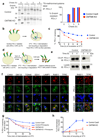
Cancer cells exploit the expression of the programmed death-1 (PD-1) ligand 1 (PD-L1) to subvert T-cell-mediated immunosurveillance. The success of therapies that disrupt PD-L1-mediated tumour tolerance has highlighted the need to understand the molecular regulation of PD-L1 expression. Here we identify the uncharacterized protein CMTM6 as a critical regulator of PD-L1 in a broad range of cancer cells, by using a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen. CMTM6 is a ubiquitously expressed protein that binds PD-L1 and maintains its cell surface expression. CMTM6 is not required for PD-L1 maturation but co-localizes with PD-L1 at the plasma membrane and in recycling endosomes, where it prevents PD-L1 from being targeted for lysosome-mediated degradation. Using a quantitative approach to profile the entire plasma membrane proteome, we find that CMTM6 displays specificity for PD-L1. Notably, CMTM6 depletion decreases PD-L1 without compromising cell surface expression of MHC class I. CMTM6 depletion, via the reduction of PD-L1, significantly alleviates the suppression of tumour-specific T cell activity in vitro and in vivo. These findings provide insights into the biology of PD-L1 regulation, identify a previously unrecognized master regulator of this critical immune checkpoint and highlight a potential therapeutic target to overcome immune evasion by tumour cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures





Comment in
-
Novel regulators of PD-L1 expression in cancer: CMTM6 and CMTM4-a new avenue to enhance the therapeutic benefits of immune checkpoint inhibitors.Ann Transl Med. 2017 Dec;5(23):467. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.09.32. Ann Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29285500 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
CMTM6 stabilizes PD-L1 expression and refines its prognostic value in tumors.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Feb;6(3):54. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.11.26. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29610746 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

