A genome-wide transcriptome map of pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) provides novel insights into salinity-related genes and marker discovery
- PMID: 28814265
- PMCID: PMC5559799
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-3989-7
A genome-wide transcriptome map of pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) provides novel insights into salinity-related genes and marker discovery
Abstract
Background: Pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) is one of the most important commercial nut crops worldwide. It is a salt-tolerant and long-lived tree, with the largest cultivation area in Iran. Climate change and subsequent increased soil salt content have adversely affected the pistachio yield in recent years. However, the lack of genomic/global transcriptomic sequences on P. vera impedes comprehensive researches at the molecular level. Hence, whole transcriptome sequencing is required to gain insight into functional genes and pathways in response to salt stress.
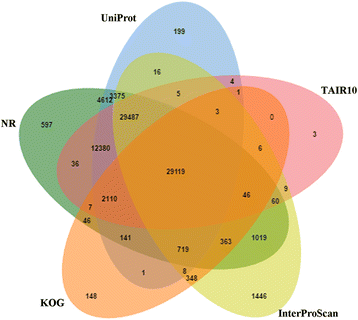
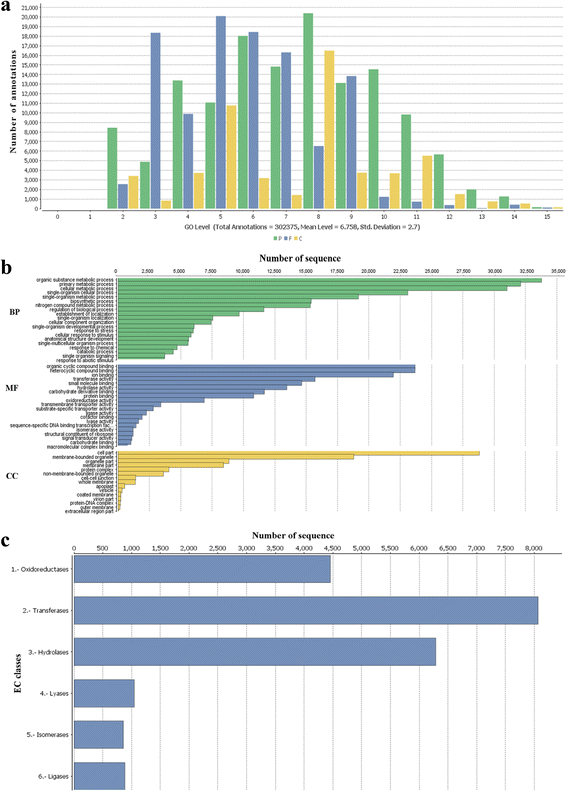
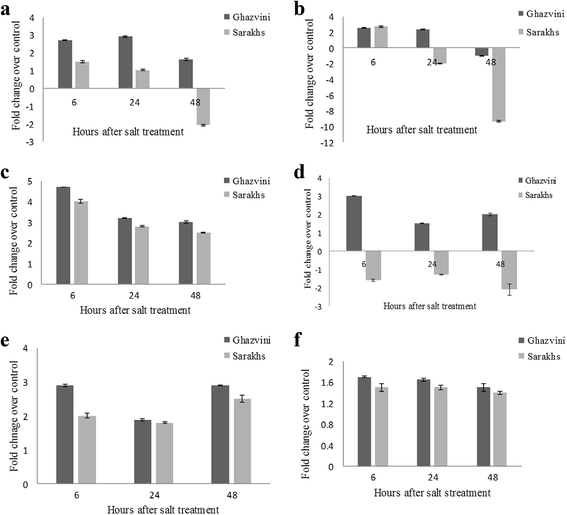
Results: RNA sequencing of a pooled sample representing 24 different tissues of two pistachio cultivars with contrasting salinity tolerance under control and salt treatment by Illumina Hiseq 2000 platform resulted in 368,953,262 clean 100 bp paired-ends reads (90 Gb). Following creating several assemblies and assessing their quality from multiple perspectives, we found that using the annotation-based metrics together with the length-based parameters allows an improved assessment of the transcriptome assembly quality, compared to the solely use of the length-based parameters. The generated assembly by Trinity was adopted for functional annotation and subsequent analyses. In total, 29,119 contigs annotated against all of five public databases, including NR, UniProt, TAIR10, KOG and InterProScan. Among 279 KEGG pathways supported by our assembly, we further examined the pathways involved in the plant hormone biosynthesis and signaling as well as those to be contributed to secondary metabolite biosynthesis due to their importance under salinity stress. In total, 11,337 SSRs were also identified, which the most abundant being dinucleotide repeats. Besides, 13,097 transcripts as candidate stress-responsive genes were identified. Expression of some of these genes experimentally validated through quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) that further confirmed the accuracy of the assembly. From this analysis, the contrasting expression pattern of NCED3 and SOS1 genes were observed between salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant cultivars.
Conclusion: This study, as the first report on the whole transcriptome survey of P. vera, provides important resources and paves the way for functional and comparative genomic studies on this major tree to discover the salinity tolerance-related markers and stress response mechanisms for breeding of new pistachio cultivars with more salinity tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A genome-wide identification, characterization and functional analysis of salt-related long non-coding RNAs in non-model plant Pistacia vera L. using transcriptome high throughput sequencing.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 27;10(1):5585. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62108-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32221354 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genomes and transcriptomes reveal adaptation and domestication of pistachio.Genome Biol. 2019 Apr 18;20(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1686-3. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 30999938 Free PMC article.
-
Genome survey of pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) by next generation sequencing: Development of novel SSR markers and genetic diversity in Pistacia species.BMC Genomics. 2016 Dec 7;17(1):998. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3359-x. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27923352 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Transcriptomics of Crop Wild Relatives to Unravel the Salinity Stress Adaptive Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 6;24(12):9813. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129813. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37372961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of salinity stress on crop plants: improving salt tolerance through genetic and molecular dissection.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Sep 15;14:1241736. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1241736. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37780527 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational screening of miRNAs and their targets in saffron (Crocus sativus L.) by transcriptome mining.Planta. 2021 Nov 9;254(6):117. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03761-7. Planta. 2021. PMID: 34751821
-
Temporal transcriptome and metabolite analyses provide insights into the biochemical and physiological processes underlying endodormancy release in pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) flower buds.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Sep 22;14:1240442. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1240442. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37810399 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide identification, characterization and functional analysis of salt-related long non-coding RNAs in non-model plant Pistacia vera L. using transcriptome high throughput sequencing.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 27;10(1):5585. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62108-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32221354 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genomes and transcriptomes reveal adaptation and domestication of pistachio.Genome Biol. 2019 Apr 18;20(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1686-3. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 30999938 Free PMC article.
-
Alkaloid production and response to natural adverse conditions in Peganum harmala: in silico transcriptome analyses.BioTechnologia (Pozn). 2022 Dec 24;103(4):355-384. doi: 10.5114/bta.2022.120706. eCollection 2022. BioTechnologia (Pozn). 2022. PMID: 36685700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zohary M. A monographical study of the genus Pistacia. Palestine J Bot (Jerusalem Ser) 1952;5(4):187–228.
-
- Crane JC. Pistachio tree nuts. Westport: Avipublishing Company; 1978.
-
- F Faostat. 2016. FAO web page. http://www.fao.org/faostat. Accessed 14 Dec 2016.
-
- Bozorgi M, Memariani Z, Mobli M, Salehi Surmaghi MH, Shams-Ardekani MR, Rahimi R. Five Pistacia species (P. vera, P. atlantica, P. terebinthus, P. khinjuk, and P. lentiscus): a review of their traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013;15:1–33. doi: 10.1155/2013/219815. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

