Public Health Literature Review of Fragile X Syndrome
- PMID: 28814537
- PMCID: PMC5621610
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-1159C
Public Health Literature Review of Fragile X Syndrome
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this systematic literature review is to describe what is known about fragile X syndrome (FXS) and to identify research gaps. The results can be used to help inform future public health research and provide pediatricians with up-to-date information about the implications of the condition for individuals and their families.
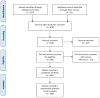
Methods: An electronic literature search was conducted, guided by a variety of key words. The search focused on 4 areas of both clinical and public health importance: (1) the full mutation phenotype, (2) developmental trajectories across the life span, (3) available interventions and treatments, and (4) impact on the family. A total of 661 articles were examined and 203 were included in the review.
Results: The information is presented in the following categories: developmental profile (cognition, language, functional skills, and transition to adulthood), social-emotional profile (cooccurring psychiatric conditions and behavior problems), medical profile (physical features, seizures, sleep, health problems, and physiologic features), treatment and interventions (educational/behavioral, allied health services, and pharmacologic), and impact on the family (family environment and financial impact). Research gaps also are presented.
Conclusions: The identification and treatment of FXS remains an important public health and clinical concern. The information presented in this article provides a more robust understanding of FXS and the impact of this complex condition for pediatricians. Despite a wealth of information about the condition, much work remains to fully support affected individuals and their families.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Malter HE, Iber JC, Willemsen R, et al. Characterization of the full fragile X syndrome mutation in fetal gametes. Nat Genet. 1997;15(2):165–169. - PubMed
-
- Loesch DZ, Huggins RM, Hagerman RJ. Phenotypic variation and FMRP levels in fragile X. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2004;10(1):31–41. - PubMed
-
- Moeschler JB, Shevell M Committee on Genetics. Comprehensive evaluation of the child with intellectual disability or global developmental delays. Pediatrics. 2014;134(3) Available at: www.pediatrics.org/cgi/content/full/134/3/e903. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hersh JH, Saul RA Committee on Genetics. Health supervision for children with fragile X syndrome. Pediatrics. 2011;127(5):994–1006. - PubMed
-
- Berry-Kravis E, Grossman AW, Crnic LS, Greenough WT. Understanding fragile X syndrome. Curr Paediatr. 2002;12(4):316–324.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical