Diabetes and dyslipidemia: characterizing lipoprotein metabolism
- PMID: 28814891
- PMCID: PMC5546776
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S115855
Diabetes and dyslipidemia: characterizing lipoprotein metabolism
Abstract
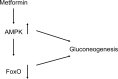
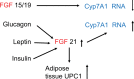
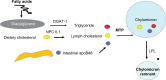
Premature atherosclerosis in diabetes accounts for much of the decreased life span. New treatments have reduced this risk considerably. This review explores the relationship among the disturbances in glucose, lipid, and bile salt metabolic pathways that occur in diabetes. In particular, excess nutrient intake and starvation have major metabolic effects, which have allowed us new insights into the disturbance that occurs in diabetes. Metabolic regulators such as the forkhead transcription factors, the farnesyl X transcription factors, and the fibroblast growth factors have become important players in our understanding of the dysregulation of metabolism in diabetes and overnutrition. The disturbed regulation of lipoprotein metabolism in both the intestine and the liver has been more clearly defined over the past few years, and the atherogenicity of the triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, and - in tandem - low levels of high-density lipoproteins, is seen now as very important. New information on the apolipoproteins that control lipoprotein lipase activity has been obtained. This is an exciting time in the battle to defeat diabetic atherosclerosis.
Keywords: dyslipidemia; farnesyl X transcription factors; fibroblast growth factor; forkhead transcription factor O1; low-density lipoprotein; obesity; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Shafrir E, Raz I. Diabetes: mellitus or lipidus? Diabetologia. 2003;46:433–440. - PubMed
-
- Despres JP, Lamarche B, Mauriège P, et al. Hyperinsulinemia as an independent risk factor for ischemic heart disease. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(15):952–957. - PubMed
-
- Zavaroni I, Bonini L, Gasparini P, et al. Hyperinsulinemia in a normal population as a predictor of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and coronary heart disease: the Barilla factory revisited. Metabolism. 1999;48(8):989–994. - PubMed
-
- Gami AS, Witt BJ, Howard DE, et al. Metabolic syndrome and risk of incident cardiovascular events and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49(4):403–414. - PubMed
-
- Reaven G. Insulin resistance and coronary heart disease in nondiabetic individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32(8):1754–1759. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

