TIA1 Mutations in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia Promote Phase Separation and Alter Stress Granule Dynamics
- PMID: 28817800
- PMCID: PMC5576574
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.07.025
TIA1 Mutations in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia Promote Phase Separation and Alter Stress Granule Dynamics
Abstract
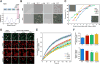
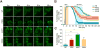
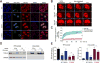
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD) are age-related neurodegenerative disorders with shared genetic etiologies and overlapping clinical and pathological features. Here we studied a novel ALS/FTD family and identified the P362L mutation in the low-complexity domain (LCD) of T cell-restricted intracellular antigen-1 (TIA1). Subsequent genetic association analyses showed an increased burden of TIA1 LCD mutations in ALS patients compared to controls (p = 8.7 × 10-6). Postmortem neuropathology of five TIA1 mutations carriers showed a consistent pathological signature with numerous round, hyaline, TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43)-positive inclusions. TIA1 mutations significantly increased the propensity of TIA1 protein to undergo phase transition. In live cells, TIA1 mutations delayed stress granule (SG) disassembly and promoted the accumulation of non-dynamic SGs that harbored TDP-43. Moreover, TDP-43 in SGs became less mobile and insoluble. The identification of TIA1 mutations in ALS/FTD reinforces the importance of RNA metabolism and SG dynamics in ALS/FTD pathogenesis.
Keywords: T cell-restricted intracellular antigen-1; TDP-43; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; frontotemporal dementia; frontotemporal lobar degeneration; liquid-liquid phase separation; low-complexity domain; membrane-less organelle; stress granules.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
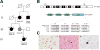
References
-
- Brand P, Dyck PJ, Liu J, Berini S, Selcen D, Milone M. Distal myopathy with coexisting heterozygous TIA1 and MYH7 Variants. Neuromuscul Disord. 2016;26:511–515. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS097273/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031581/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS092091/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P01 NS084974/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS097261/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS076471/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS097974/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS072248/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

