Evaluating the effect of immune cells on the outcome of patients with mesothelioma
- PMID: 28817839
- PMCID: PMC5672927
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2017.269
Evaluating the effect of immune cells on the outcome of patients with mesothelioma
Abstract
Background: We systematically assessed the prognostic and predictive value of infiltrating adaptive and innate immune cells in a large cohort of patients with advanced mesothelioma.
Methods: A tissue microarray from 302 samples was constructed. Markers of adaptive immune response in T-cells (CD8+, FOXP3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD3+) and B-cells (CD20+), and of innate immune response; neutrophils (NP57+), natural killer cells (CD56+) and macrophages (CD68+) were evaluated.
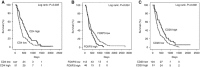
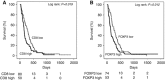
Results: We found that in the epithelioid tumours, high CD4+ and CD20+ counts, and low FOXP3+, CD68+ and NP57+ counts linked to better outcome. In the non-epithelioid group low CD8+ and low FOXP3+ counts were beneficial.On multivariate analysis low FOXP3+ remained independently associated with survival in both groups. In the epithelioid group additionally high CD4+, high CD20+, and low NP57+ counts were prognostic.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate for the first time, in predominately advanced disease, the association of key markers of adaptive and innate immunity with survival and the differential effect of histology. A better understanding of the immunological drivers of the different subtypes of mesothelioma will assist prognostication and disease-specific clinical decision-making.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alley EW, Lopez J, Santoro A, Morosky A, Saraf S, Piperdi B, van Brummelen E (2017) Clinical safety and activity of pembrolizumab in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (KEYNOTE-028): preliminary results from a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Onco 18(5): 623–630. - PubMed
-
- Al Shibli KI, Donnem T, Al-Saad S, Persson M, Bremnes RM, Busund LT (2008) Prognostic effect of epithelial and stromal lymphocyte infiltration in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(16): 5220–5227. - PubMed
-
- Anraku M, Cunningham KS, Yun Z, Tsao MS, Zhang L, Keshavjee S, Johnston MR, de Perrot M (2008) Impact of tumour-infiltrating T-cells on survival in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 135(4): 823–829. - PubMed
-
- Awad MM, Jones RE, Liu H, Lizotte PH, Ivanova EV, Kulkarni M, Herter-Sprie GS, Liao X, Santos AA, Bittinger MA, Keogh L, Koyama S, Almonte C, English JM, Barlow J, Richards WG, Barbie DA, Bass AJ, Rodig SJ, Hodi FS, Wucherpfennig KW, Jänne PA, Sholl LM, Hammerman PS, Wong KK, Bueno R (2016) Cytotoxic T cells in PD-L1 positive malignant pleural mesotheliomas are counterbalanced by distinct immunosuppressive factors. Cancer Immunol Res 4(12): 1038–1048. - PubMed
-
- Badoual C, Hans S, Rodriguez J, Peyrard S, Klein C, Agueznay NEH, Mosseri V, Laccourreye O, Bruneval P, Fridman WH, Brasnu DF, Tartour E (2006) Prognostic value of tumour-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell subpopulations in head and neck cancers. Clin Cancer Res 12(2): 465–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

