Auxin Signaling
- PMID: 28818861
- PMCID: PMC5761761
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.17.00765
Auxin Signaling
Abstract
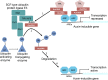
Auxin triggers diverse responses in plants, and this is reflected in quantitative and qualitative diversity in the auxin signaling machinery.
Figures

References
-
- Abley K, De Reuille PB, Strutt D, Bangham A, Prusinkiewicz P, Marée AF, Grieneisen VA, Coen E (2013) An intracellular partitioning-based framework for tissue cell polarity in plants and animals. Development 140: 2061–2074 - PubMed
-
- Badescu GO, Napier RM (2006) Receptors for auxin: Will it all end in TIRs? Trends Plant Sci 11: 217–223 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

