A practical guide to single-cell RNA-sequencing for biomedical research and clinical applications
- PMID: 28821273
- PMCID: PMC5561556
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-017-0467-4
A practical guide to single-cell RNA-sequencing for biomedical research and clinical applications
Abstract
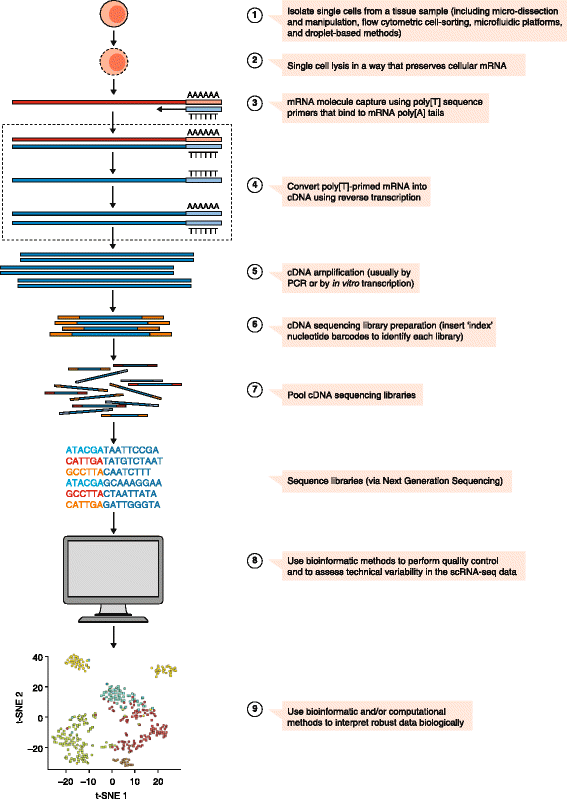
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) is a genomic approach for the detection and quantitative analysis of messenger RNA molecules in a biological sample and is useful for studying cellular responses. RNA-seq has fueled much discovery and innovation in medicine over recent years. For practical reasons, the technique is usually conducted on samples comprising thousands to millions of cells. However, this has hindered direct assessment of the fundamental unit of biology-the cell. Since the first single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) study was published in 2009, many more have been conducted, mostly by specialist laboratories with unique skills in wet-lab single-cell genomics, bioinformatics, and computation. However, with the increasing commercial availability of scRNA-seq platforms, and the rapid ongoing maturation of bioinformatics approaches, a point has been reached where any biomedical researcher or clinician can use scRNA-seq to make exciting discoveries. In this review, we present a practical guide to help researchers design their first scRNA-seq studies, including introductory information on experimental hardware, protocol choice, quality control, data analysis and biological interpretation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
TL has given an invited talk at an Industry Sponsored Symposium at the 4th European Congress of Immunology in 2015. His congress participation was reimbursed by Fluidigm Inc. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

