Frontline ADAPT therapy to treat patients with symptomatic M2 and M3 occlusions in acute ischemic stroke: initial experience with the Penumbra ACE and 3MAX reperfusion system
- PMID: 28821628
- PMCID: PMC5909737
- DOI: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013233
Frontline ADAPT therapy to treat patients with symptomatic M2 and M3 occlusions in acute ischemic stroke: initial experience with the Penumbra ACE and 3MAX reperfusion system
Abstract
Background: After a series of positive studies for mechanical thrombectomy in large vessel occlusion acute ischemic stroke, the question remains, can symptomatic patients with distal vessel occlusion benefit from mechanical thrombectomy?
Purpose: To assess the safety and efficacy of the 3MAX reperfusion system as frontline therapy for M2 and M3 occlusions.
Methods: This study retrospectively collected data on 58 patients treated for M2 and M3 occlusions between January and September 2016. Of these 58 patients, 31 had an isolated M2 or M3 occlusion. Eligible patients were treated with 3MAX by adirect first pass aspiration (ADAPT) technique within 6 hours following stroke onset. Effectiveness was defined by functional independence (90-day modified Rankin Scale core 0-2) and revascularization to modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction (mTICI) 2b-3 scores adjudicated by a core laboratory, while complication rates were used to determine safety of the device and the procedure.
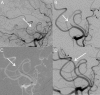
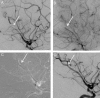
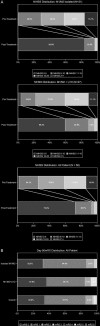
Results: Patients with an isolated M2 or M3 occlusion had a mean age of 68.6±13.3 years (range 18-90 years), a median National Institutes of Health Stroke Score of 15 (IQR 9-19), and ASPECTS score of 9 (IQR 8-10). After intervention, 100% (31/31) of patients were revascularized to mTICI 2b-3; 77.4% (24/31) of patients showed revascularization to mTICI 3. Aspiration alone led to revascularization in 83.9% (26/31) of patients. At 90 days, 96.8% (30/31) of patients had achieved functional independence. The incidence of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage was 0% (0/31).
Conclusions: Results suggest that the 3MAX reperfusion system is safe and effective in achieving successful revascularization and functional independence for patients with acute ischemic stroke secondary to M2 and M3 occlusions using ADAPT, either as frontline monotherapy, or in combination with adjunctive devices.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; aspiration thrombectomy; distal occlusion; endovascular therapy.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JA: Travel support for presentation at congresses, PENUMBRA; J-OK, SH, RH, CL: None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comparative analysis of 3MAX aspiration versus 3 mm Trevo Retriever for distal occlusion thrombectomy in acute stroke.J Neurointerv Surg. 2020 Mar;12(3):279-282. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-014990. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020. PMID: 31243066
-
Contact Aspiration Versus Stent Retriever in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke With M2 Occlusion in the ASTER Randomized Trial (Contact Aspiration Versus Stent Retriever for Successful Revascularization).Stroke. 2018 Feb;49(2):461-464. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.019598. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Stroke. 2018. PMID: 29284735 Clinical Trial.
-
Mechanical thrombectomy of M2 occlusions with distal access catheters using ADAPT.J Neuroradiol. 2019 Jul;46(4):231-237. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2019.01.096. Epub 2019 Feb 13. J Neuroradiol. 2019. PMID: 30771378
-
Revascularization of tandem occlusions in acute ischemic stroke: review of the literature and illustrative case.Neurosurg Focus. 2017 Apr;42(4):E15. doi: 10.3171/2017.1.FOCUS16521. Neurosurg Focus. 2017. PMID: 28366063 Review.
-
A Retrospective Single-Center Case Series of Direct Aspiration Thrombectomy as First-Line Approach in Ischemic Stroke and Review of the Literature.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019 Mar;28(3):640-648. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.11.004. Epub 2018 Dec 19. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 30579732 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Mechanical Thrombectomy Using an Aspiration Catheter Compared with a Stent Retriever Alone for Middle Cerebral Artery M2 Occlusion.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022;16(12):593-599. doi: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2022-0035. Epub 2022 Oct 29. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022. PMID: 37502667 Free PMC article.
-
3MAX catheter for thromboaspiration of downstream and new territory emboli after mechanical thrombectomy of large vessel occlusions: initial experience.Interv Neuroradiol. 2019 Jun;25(3):277-284. doi: 10.1177/1591019918811802. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Interv Neuroradiol. 2019. PMID: 30463503 Free PMC article.
-
AQURE PASSPORT Intracranial Catheter for Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients.J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2019 May;10(3):46-52. J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31308871 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular Device Choice and Tools for Recanalization of Medium Vessel Occlusions: Insights From the MeVO FRONTIERS International Survey.Front Neurol. 2021 Sep 15;12:735899. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.735899. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34603187 Free PMC article.
-
First-Line A Direct Aspiration First-Pass Technique vs. First-Line Stent Retriever for Acute Ischemic Stroke Therapy: A Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2018 Sep 25;9:801. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00801. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30319531 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
