Contribution of Astroglial Cx43 Hemichannels to the Modulation of Glutamatergic Currents by D-Serine in the Mouse Prefrontal Cortex
- PMID: 28821660
- PMCID: PMC6596802
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2204-16.2017
Contribution of Astroglial Cx43 Hemichannels to the Modulation of Glutamatergic Currents by D-Serine in the Mouse Prefrontal Cortex
Abstract
Astrocytes interact dynamically with neurons by modifying synaptic activity and plasticity. This interplay occurs through a process named gliotransmission, meaning that neuroactive molecules are released by astrocytes. Acting as a gliotransmitter, D-serine, a co-agonist of the NMDA receptor at the glycine-binding site, can be released by astrocytes in a calcium [Ca2+]i-dependent manner. A typical feature of astrocytes is their high expression level of connexin43 (Cx43), a protein forming gap junction channels and hemichannels associated with dynamic neuroglial interactions. Pharmacological and genetic inhibition of Cx43 hemichannel activity reduced the amplitude of NMDA EPSCs in mouse layer 5 prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons without affecting AMPA EPSC currents. This reduction of NMDA EPSCs was rescued by addition of D-serine in the extracellular medium. LTP of NMDA and AMPA EPSCs after high-frequency stimulation was reduced by prior inhibition of Cx43 hemichannel activity. Inactivation of D-serine synthesis within the astroglial network resulted in the reduction of NMDA EPSCs, which was rescued by adding extracellular D-serine. We showed that the activity of Cx43 hemichannels recorded in cultured astrocytes was [Ca2+]I dependent. Accordingly, in acute cortical slices, clamping [Ca2+]i at a low level in astroglial network resulted in an inhibition of NMDA EPSC potentiation that was rescued by adding extracellular D-serine. This work demonstrates that astroglial Cx43 hemichannel activity is associated with D-serine release. This process, occurring by direct permeation of D-serine through hemichannels or indirectly by Ca2+ entry and activation of other [Ca2+]i-dependent mechanisms results in the modulation of synaptic activity and plasticity.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT We recorded neuronal glutamatergic (NMDA and AMPA) responses in prefrontal cortex (PFC) neurons and used pharmacological and genetic interventions to block connexin-mediated hemichannel activity specifically in a glial cell population. For the first time in astrocytes, we demonstrated that hemichannel activity depends on the intracellular calcium concentration and is associated with D-serine release. Blocking hemichannel activity reduced the LTP of these excitatory synaptic currents triggered by high-frequency stimulation. These observations may be particularly relevant in the PFC, where D-serine and its converting enzyme are highly expressed.
Keywords: astrocyte; connexin; gliotransmitter; hemichannel; neuroglial interaction; prefrontal cortex.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/379064-12$15.00/0.
Figures




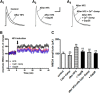


Similar articles
-
The role of astrocytes in depression, its prevention, and treatment by targeting astroglial gliotransmitter release.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2307953121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2307953121. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39495924 Free PMC article.
-
Astroglial gliotransmitters released via Cx43 hemichannels regulate NMDAR-dependent transmission and short-term fear memory in the basolateral amygdala.FASEB J. 2022 Feb;36(2):e22134. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100798RR. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35061296
-
Astroglial connexin43 hemichannels tune basal excitatory synaptic transmission.J Neurosci. 2014 Aug 20;34(34):11228-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0015-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25143604 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insight into astrocyte-mediated gliotransmission modulates the synaptic plasticity in major depressive disorder.Life Sci. 2024 Oct 15;355:122988. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122988. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39153595 Review.
-
Connexin targeting peptides as inhibitors of voltage- and intracellular Ca2+-triggered Cx43 hemichannel opening.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:506-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.021. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 24007825 Review.
Cited by
-
Connexins in Cardiovascular and Neurovascular Health and Disease: Pharmacological Implications.Pharmacol Rev. 2017 Oct;69(4):396-478. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.012062. Pharmacol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28931622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute activation of hemichannels by ethanol leads to Ca2+-dependent gliotransmitter release in astrocytes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 21;12:1422978. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1422978. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38974144 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting gliovascular connexins prevents inflammatory blood-brain barrier leakage and astrogliosis.JCI Insight. 2022 Aug 22;7(16):e135263. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.135263. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35881483 Free PMC article.
-
Increased thin-spine density in frontal cortex pyramidal neurons in a genetic rat model of schizophrenia-relevant features.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021 Mar;44:79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2021.01.006. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33485732 Free PMC article.
-
The role of astrocytes in depression, its prevention, and treatment by targeting astroglial gliotransmitter release.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2307953121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2307953121. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39495924 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
