TNF-α-induced Inflammation Stimulates Apolipoprotein-A4 via Activation of TNFR2 and NF-κB Signaling in Kidney Tubular Cells
- PMID: 28821873
- PMCID: PMC5562825
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-08785-2
TNF-α-induced Inflammation Stimulates Apolipoprotein-A4 via Activation of TNFR2 and NF-κB Signaling in Kidney Tubular Cells
Abstract
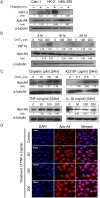
Apo-A4 expression was increased in tissues from chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients compared to that in normal kidney tissue. We determined the association of apo-A4 and its regulatory signals following acute kidney injury and elucidated the effects of apo-A4 on cell signaling pathways related to kidney injury in vitro and in vivo. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, which causes inflammatory cell injury, induced significantly increased expression of apo-A4 protein levels, and these levels were related to pro-inflammatory acute kidney injury in human kidney cells. Apo-A4 expression was also increased in experimented rat kidney tissues after ischemic reperfusion injury. The expression of tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) 2 was increased in both kidney cell lines and experimented rat kidney tissues following acute kidney injury. The expression of apo-A4 and TNFR2 was increased upon treatment with TNF-α. Immunohistochemistry revealed positive apo-A4 and TNFR2 staining in ischemic reperfusion injury rat kidneys compared with levels in the sham operation kidneys. After neutralization of TNF-α, NF-κB expression was only observed in the cytoplasm by immunofluorescence. Therefore, the apo-A4 expression is increased by stimulation of injured kidney cells with TNF-α and that these effects occur via a TNFR2-NFκB complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Signaling pathway via TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB in intestinal epithelial cells may be directly involved in colitis-associated carcinogenesis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Apr;296(4):G850-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00071.2008. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19179628
-
TNFR2 increases the sensitivity of ligand-induced activation of the p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways and signals TRAF2 protein degradation in macrophages.Cell Signal. 2014 Apr;26(4):683-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.12.009. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24378531
-
TNFR2 interposes the proliferative and NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response by podocytes to TNF-α.Lab Invest. 2011 Mar;91(3):413-25. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.199. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Lab Invest. 2011. PMID: 21221075 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-κB, MAP kinases and cell death.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26993379 Review.
-
TNF/TNFR: drug target for autoimmune diseases and immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014 Jun 1;19(7):1028-40. doi: 10.2741/4265. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014. PMID: 24896334 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Panel of Serum-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles for the Screening and Diagnosis of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 30;14(15):3719. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153719. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35954383 Free PMC article.
-
Chenopodium botrys Extract Affects Acute Kidney Injury Caused by Rhabdomyolysis in Rats Through TNF/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Dec 10;13(1):e4667. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4667. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39803217 Free PMC article.
-
Precision nephrology identified tumor necrosis factor activation variability in minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.Kidney Int. 2023 Mar;103(3):565-579. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.10.023. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Kidney Int. 2023. PMID: 36442540 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics Analysis for Identification of Potential Cell Signaling Pathways and Protein Targets of Actions of Atractylodin and β-Eudesmol Against Cholangiocarcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Mar 1;21(3):621-628. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.3.621. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32212786 Free PMC article.
-
Phytosterol organic acid esters: Characterization, anti-inflammatory properties and a delivery strategy to improve mitochondrial function.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Feb 26;8:100702. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100702. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 38487178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kronenberg F, et al. Apolipoprotein A-IV serum concentrations are elevated in patients with mild and moderate renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:461–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

