In situ imaging reveals properties of purinergic signalling in trigeminal sensory ganglia in vitro
- PMID: 28822016
- PMCID: PMC5714839
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-017-9576-1
In situ imaging reveals properties of purinergic signalling in trigeminal sensory ganglia in vitro
Abstract
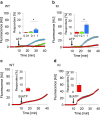
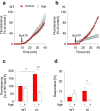
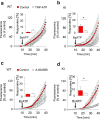
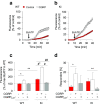
Chronic pain is supported by sterile inflammation that induces sensitisation of sensory neurons to ambient stimuli including extracellular ATP acting on purinergic P2X receptors. The development of in vitro methods for drug screening would be useful to investigate cell crosstalk and plasticity mechanisms occurring during neuronal sensitisation and sterile neuroinflammation. Thus, we studied, at single-cell level, membrane pore dilation based on the uptake of a fluorescent probe following sustained ATP-gated P2X receptor function in neurons and non-neuronal cells of trigeminal ganglion cultures from wild-type (WT) and R192Q CaV2.1 knock-in (KI) mice, a model of familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 characterised by neuronal sensitisation and higher release of soluble mediators. In WT cultures, pore responses were mainly evoked by ATP rather than benzoyl-ATP (BzATP) and partly inhibited by the P2X antagonist TNP-ATP. P2X7 receptors were expressed in trigeminal ganglia mainly by non-neuronal cells. In contrast, KI cultures showed higher expression of P2X7 receptors, stronger responses to BzATP, an effect largely prevented by prior administration of CaV2.1 blocker ω-agatoxin IVA, small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based silencing of P2X7 receptors or the P2X7 antagonist A-804598. No cell toxicity was detected with the protocols. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a well-known migraine mediator, potentiated BzATP-evoked membrane permeability in WT as well as R192Q KI cultures, demonstrating its modulatory role on trigeminal sensory ganglia. Our results show an advantageous experimental approach to dissect pharmacological properties potentially relevant to chronic pain and suggest that CGRP is a soluble mediator influencing purinergic P2X pore dilation and regulating inflammatory responses.
Keywords: ATP; CACNA1A; DRG; FHM1; Migraine; P2X3; P2X7; Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Arletta Nowodworska declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Arn M. J. M. van den Maagdenberg declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Andrea Nistri declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Elsa Fabbretti declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal procedures were in accordance with national regulations of animal welfare and approved by the ethics committee of the International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA).
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

