Preoperative anemia associated with adverse outcomes after infrainguinal bypass surgery in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia
- PMID: 28822661
- PMCID: PMC5701845
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.05.103
Preoperative anemia associated with adverse outcomes after infrainguinal bypass surgery in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia
Abstract
Objective: Preoperative anemia in elderly patients undergoing surgery is prevalent and associated with adverse events; however, the interaction with other risk factors in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) is not well described. The purpose of this study was to assess the association between lower hematocrit (HCT) levels on admission and postoperative outcomes after infrainguinal bypass surgery.
Methods: Patients with CLTI undergoing nonemergent infrainguinal bypass were identified in the targeted vascular module of National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP; 2011-2014). The 30-day outcomes were compared across preoperative HCT levels: severe (≤29%), moderate (29.1%-34%), mild (34.1%-39%), or no anemia (>39%), with no anemia serving as the reference group for all analyses. Independent associations between levels of anemia and postoperative outcomes were established using multivariable logistic regression. A sensitivity analysis was performed to assess interactions between preoperative anemia and blood transfusions.
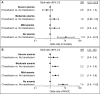
Results: We identified 5081 patients undergoing bypass, of which 741 (15%) had severe, 1317 (26%) moderate, 1516 (30%) mild, and 1507 (30%) no anemia. Anemic patients were older and more commonly suffered from tissue loss and comorbidities (eg, hypertension, diabetes, and renal insufficiency; all P < .001). After adjustment for baseline conditions, mortality was higher in those with severe anemia (3.1%; odds ratio [OR], 2.8; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.3-6.3) and moderate anemia (3.0%; OR, 2.6; 95% CI, 1.2-5.5) compared with those without anemia (0.7%). Severe anemia was independently associated with major amputation (6.9% vs 3.3%; OR, 1.6; 95% CI, 1.01-2.6) compared with no anemia. Anemia on admission was additionally associated with several other adverse outcomes, such as major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE; severe: OR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.1-3.0; moderate: OR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.3-2.9; mild: OR, 1.6; 95% CI, 1.1-2.4) and unplanned return to the operating room (severe: OR, 1.6; 95% CI, 1.2-2.1; moderate: OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2-1.8; mild, OR: 1.3; 95% CI, 1.03-1.6). Moreover, mortality associated with preoperative anemia was not different in patients receiving postoperative blood transfusions compared with those who did not, whereas MACE was significantly higher in patients with preoperative anemia and blood transfusions (interaction; P < .001).
Conclusions: Mortality and major adverse events in CLTI patients undergoing infrainguinal bypass are inversely associated with preoperative HCT levels, with the highest event rates in the most severely anemic patients. The correlation between anemia and MACE-but not mortality-was stronger in those patients receiving postoperative blood transfusions. Further research is needed to define an appropriate transfusion threshold, and attention should be focused on how to best optimize anemic CLTI patients before intervention.
Copyright © 2017 Society for Vascular Surgery. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Baron DM, Hochrieser H, Posch M, Metnitz B, Rhodes A, Moreno RP, et al. Preoperative anaemia is associated with poor clinical outcome in non-cardiac surgery patients. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113(3):416–423. - PubMed
-
- Corwin HL, Gettinger A, Pearl RG, Fink MP, Levy MM, Abraham E, et al. The CRIT Study: Anemia and blood transfusion in the critically ill--current clinical practice in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(1):39–52. - PubMed
-
- Shander A, Knight K, Thurer R, Adamson J, Spence R. Prevalence and outcomes of anemia in surgery: a systematic review of the literature. Am J Med. 2004;116(Suppl 7A):58S–69S. - PubMed
-
- Shander A, Javidroozi M, Ozawa S, Hare GM. What is really dangerous: anaemia or transfusion? Br J Anaesth. 2011;107(Suppl 1):i41–59. - PubMed
-
- Carson JL, Duff A, Poses RM, Berlin JA, Spence RK, Trout R, et al. Effect of anaemia and cardiovascular disease on surgical mortality and morbidity. Lancet. 1996;348(9034):1055–1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

