Temporal dynamics of cardiac hypertrophic growth in response to pressure overload
- PMID: 28822967
- PMCID: PMC6148204
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00284.2017
Temporal dynamics of cardiac hypertrophic growth in response to pressure overload
Abstract
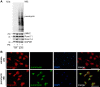
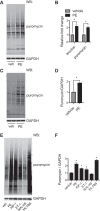
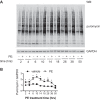
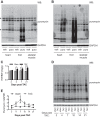
Hypertension is one of the most important risk factors of heart failure. In response to high blood pressure, the left ventricle manifests hypertrophic growth to ameliorate wall stress, which may progress into decompensation and trigger pathological cardiac remodeling. Despite the clinical importance, the temporal dynamics of pathological cardiac growth remain elusive. Here, we took advantage of the puromycin labeling approach to measure the relative rates of protein synthesis as a way to delineate the temporal regulation of cardiac hypertrophic growth. We first identified the optimal treatment conditions for puromycin in neonatal rat ventricular myocyte culture. We went on to demonstrate that myocyte growth reached its peak rate after 8-10 h of growth stimulation. At the in vivo level, with the use of an acute surgical model of pressure-overload stress, we observed the maximal growth rate to occur at day 7 after surgery. Moreover, RNA sequencing analysis supports that the most profound transcriptomic changes occur during the early phase of hypertrophic growth. Our results therefore suggest that cardiac myocytes mount an immediate growth response in reply to pressure overload followed by a gradual return to basal levels of protein synthesis, highlighting the temporal dynamics of pathological cardiac hypertrophic growth.NEW & NOTEWORTHY We determined the optimal conditions of puromycin incorporation in cardiac myocyte culture. We took advantage of this approach to identify the growth dynamics of cardiac myocytes in vitro. We went further to discover the protein synthesis rate in vivo, which provides novel insights about cardiac temporal growth dynamics in response to pressure overload.
Keywords: cardiac myocyte; growth dynamics; pathological cardiac hypertrophy; pressure overload; puromycin.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Jordan LC, Judd SE, Lackland D, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth L, Liu S, Longenecker CT, Mackey RH, Matsushita K, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Thiagarajan RR, Reeves MJ, Ritchey M, Rodriguez CJ, Roth GA, Rosamond WD, Sasson C, Towfighi A, Tsao CW, Turner MB, Virani SS, Voeks JH, Willey JZ, Wilkins JT, Wu JH, Alger HM, Wong SS, Muntner P; American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee . Heart disease and stroke statistics−2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 135: e146–e603, 2017. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

