How empathic is your healthcare practitioner? A systematic review and meta-analysis of patient surveys
- PMID: 28823250
- PMCID: PMC5563892
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-017-0967-3
How empathic is your healthcare practitioner? A systematic review and meta-analysis of patient surveys
Abstract
Background: A growing body of evidence suggests that healthcare practitioners who enhance how they express empathy can improve patient health, and reduce medico-legal risk. However we do not know how consistently healthcare practitioners express adequate empathy. In this study, we addressed this gap by investigating patient rankings of practitioner empathy.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies that asked patients to rate their practitioners' empathy using the Consultation and Relational Empathy (CARE) measure. CARE is emerging as the most common and best-validated patient rating of practitioner empathy. We searched: MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, Cinahl, Science & Social Science Citation Indexes, the Cochrane Library and PubMed from database inception to March 2016. We excluded studies that did not use the CARE measure. Two reviewers independently screened titles and extracted data on average CARE scores, demographic data for patients and practitioners, and type of healthcare practitioners.
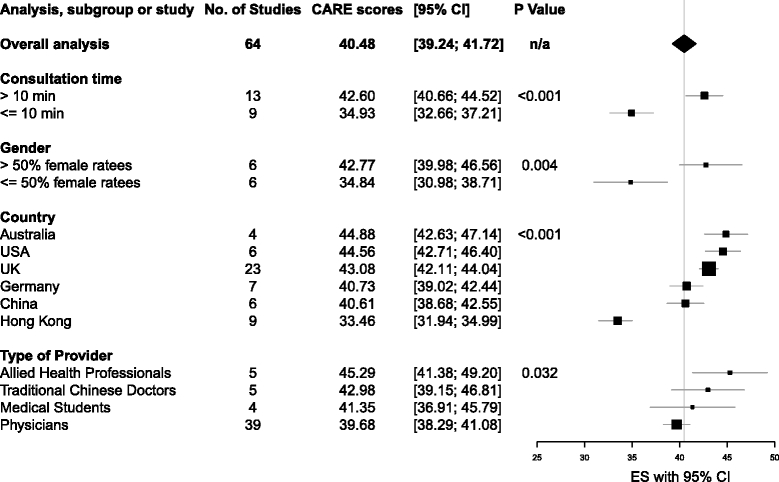
Results: Sixty-four independent studies within 51 publications had sufficient data to pool. The average CARE score was 40.48 (95% CI, 39.24 to 41.72). This rank s in the bottom 5th percentile in comparison with scores collected by CARE developers. Longer consultations (n = 13) scored 15% higher (42.60, 95% CI 40.66 to 44.54) than shorter (n = 9) consultations (34.93, 95% CI 32.63 to 37.24). Studies with mostly (>50%) female practitioners (n = 6) showed 16% higher empathy scores (42.77, 95% CI 38.98 to 46.56) than those with mostly (>50%) male (n = 6) practitioners (34.84, 95% CI 30.98 to 38.71). There were statistically significant (P = 0.032) differences between types of providers (allied health professionals, medical students, physicians, and traditional Chinese doctors). Allied Health Professionals (n = 6) scored the highest (45.29, 95% CI 41.38 to 49.20), and physicians (n = 39) scored the lowest (39.68, 95% CI 38.29 to 41.08). Patients in Australia, the USA, and the UK reported highest empathy ratings (>43 average CARE), with lowest scores (<35 average CARE scores) in Hong Kong.
Conclusions: Patient rankings of practitioner empathy are highly variable, with female practitioners expressing empathy to patients more effectively than male practitioners. The high variability of patient rating of practitioner empathy is likely to be associated with variable patient health outcomes. Limitations included frequent failure to report response rates introducing a risk of response bias. Future work is warranted to investigate ways to reduce the variability in practitioner empathy.
Keywords: Communication; Consultation; Empathy; Expectations; Practitioner.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not relevant (systematic review).
Consent for publication
Not relevant (systematic review).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Chassany O, Boureau F, Liard F, Bertin P, Serrie A, Ferran P, Keddad K, Jolivet-Landreau I, Marchand S. Effects of training on general practitioners' management of pain in osteoarthritis: a randomized multicenter study. J Rheumatol. 2006;33(9):1827–1834. - PubMed
-
- Fujimori M, Shirai Y, Asai M, Kubota K, Katsumata N, Uchitomi Y. Effect of communication skills training program for oncologists based on patient preferences for communication when receiving bad news: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(20):2166–2172. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.51.2756. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous