Activation and Desensitization Mechanism of AMPA Receptor-TARP Complex by Cryo-EM
- PMID: 28823560
- PMCID: PMC5621841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.045
Activation and Desensitization Mechanism of AMPA Receptor-TARP Complex by Cryo-EM
Abstract
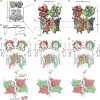
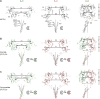
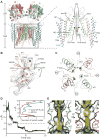
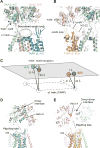
AMPA receptors mediate fast excitatory neurotransmission in the mammalian brain and transduce the binding of presynaptically released glutamate to the opening of a transmembrane cation channel. Within the postsynaptic density, however, AMPA receptors coassemble with transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory proteins (TARPs), yielding a receptor complex with altered gating kinetics, pharmacology, and pore properties. Here, we elucidate structures of the GluA2-TARP γ2 complex in the presence of the partial agonist kainate or the full agonist quisqualate together with a positive allosteric modulator or with quisqualate alone. We show how TARPs sculpt the ligand-binding domain gating ring, enhancing kainate potency and diminishing the ensemble of desensitized states. TARPs encircle the receptor ion channel, stabilizing M2 helices and pore loops, illustrating how TARPs alter receptor pore properties. Structural and computational analysis suggests the full agonist and modulator complex harbors an ion-permeable channel gate, providing the first view of an activated AMPA receptor.
Keywords: chemical synapse; glutamate receptor; ion channel gating; ligand gated ion channel; membrane protein; neurotransmitter; structural biology; synapse.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Armstrong N, Gouaux E. Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: crystal structures of the GluR2 ligand binding core. Neuron. 2000;28:165–181. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N, Jasti J, Beich-Frandsen M, Gouaux E. Measurement of conformational changes accompanying desensitization in an ionotropic glutamate receptor. Cell. 2006;127:85–97. - PubMed
-
- Bowie D, Mayer ML. Inward recification of both AMPA and kainate subtype glutamate receptors generated by polyamine-mediated ion channel block. Neuron. 1995;15:453–462. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

