Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus Persistence
- PMID: 28823759
- PMCID: PMC5741523
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.07.006
Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus Persistence
Abstract
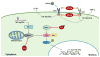
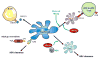
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects 250 million people worldwide, resulting in nearly one million deaths annually. Studies in recent years have significantly improved our knowledge on the mechanisms of HBV persistence. HBV uses multiple pathways to harness host innate immunity to enhance its replication. It can also take advantage of the developing immune system and the not-yet-stabilized gut microbiota of young children to facilitate its persistence, and use maternal viral e antigen to educate immunity of the offspring to support its persistence after vertical transmission. The knowledge gained from these recent studies paves the way for the development of new therapies for the treatment of chronic HBV infection, which has so far been very challenging.
Keywords: HBV e antigen; age and maternal effects; chronic hepatitis B; interferon immune responses; vertical transmission.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Global Hepatitis Report 2017. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2017.
-
- Milich D, Liang TJ. Exploring the biological basis of hepatitis B e antigen in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2003;38(5):1075–86. - PubMed
-
- Ou JH. Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus e antigen. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1997;12(9–10):S178–87. - PubMed
-
- Shin EC, et al. Immune responses and immunopathology in acute and chronic viral hepatitis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16(8):509–23. - PubMed
-
- Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2006;1:23–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

