MicroRNA Expression Analysis of Centenarians and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Reveals a Common Expression Pattern
- PMID: 28824293
- PMCID: PMC5562112
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.18972
MicroRNA Expression Analysis of Centenarians and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Reveals a Common Expression Pattern
Abstract
Micro-RNA (miRNA) are a family of small non-coding ribonucleic acids that inhibits post-transcriptionally the expression of their target messenger RNA (mRNA). We are interested in studying the involvement of miRNA in longevity and autoimmune diseases. In this study we compared the different expression of seven microRNAs between human plasma healthy controls, plasma samples of centenarians and samples from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. We used the Life Technologies' protocol to quantify seven miRNAs from 62 plasma samples: 20 healthy human controls, 14 centenarians, 28 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. TaqMan MicroRNA assays were used to analyze the expression profiles of miR-125b-5p, miR-425-5p, miR-200b5p, miR-200c-3p, miR-579-3p, miR-212-3p, miR-21-5p and miR-126-3p. The relative expression of mature miRNAs was analyzed using software REST. Our results show that miR-425-5p, miR-21 and miR-212 significantly decreased in centenarians and in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with controls. Furthermore in this work we highlight a connection between corticosteroid treatment and miRNAs expression.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; centenarians; glucocorticoids; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
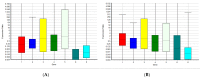
 : activation of metabolic way.
: activation of metabolic way.References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Boehm M, Slack FA. Developmental timing microRNA and its target regulate life span in C. elegans. Science. 2005;310(5756):1954–1957. - PubMed
-
- Ibanez-Ventoso C, Yang M, Guo S, Robins H, Padgett RW, Driscoll M. Modulated microRNA expression during adult lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell. 2006;5(3):235–246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

