Tissue-specific regulation of BMP signaling by Drosophila N-glycanase 1
- PMID: 28826503
- PMCID: PMC5599231
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.27612
Tissue-specific regulation of BMP signaling by Drosophila N-glycanase 1
Abstract
Mutations in the human N-glycanase 1 (NGLY1) cause a rare, multisystem congenital disorder with global developmental delay. However, the mechanisms by which NGLY1 and its homologs regulate embryonic development are not known. Here we show that Drosophila Pngl encodes an N-glycanase and exhibits a high degree of functional conservation with human NGLY1. Loss of Pngl results in developmental midgut defects reminiscent of midgut-specific loss of BMP signaling. Pngl mutant larvae also exhibit a severe midgut clearance defect, which cannot be fully explained by impaired BMP signaling. Genetic experiments indicate that Pngl is primarily required in the mesoderm during Drosophila development. Loss of Pngl results in a severe decrease in the level of Dpp homodimers and abolishes BMP autoregulation in the visceral mesoderm mediated by Dpp and Tkv homodimers. Thus, our studies uncover a novel mechanism for the tissue-specific regulation of an evolutionarily conserved signaling pathway by an N-glycanase enzyme.
Keywords: BMP signaling; D. melanogaster; Drosophila; NGLY1; developmental biology; midgut; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures


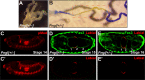

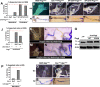
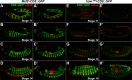


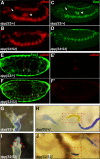
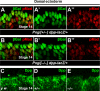
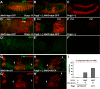





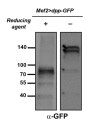
Comment in
-
Enzymatic insights into an inherited genetic disorder.Elife. 2017 Sep 14;6:e31127. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31127. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28910263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi-Yamada T, Nakamura M, Irie K, Tomoyasu Y, Sano Y, Mori E, Goto S, Ueno N, Nishida Y, Matsumoto K. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase can be involved in transforming growth factor beta superfamily signal transduction in Drosophila wing morphogenesis. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 1999;19:2322–2329. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.2322. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aoki H, Fujii M, Imamura T, Yagi K, Takehara K, Kato M, Miyazono K. Synergistic effects of different bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors on alkaline phosphatase induction. Journal of Cell Science. 2001;114:1483–1489. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

