Multifarious Functions of the Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein
- PMID: 28826631
- PMCID: PMC5610095
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tig.2017.07.008
Multifarious Functions of the Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein
Abstract
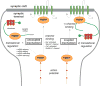
Fragile X syndrome (FXS), a heritable intellectual and autism spectrum disorder (ASD), results from the loss of Fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP). This neurodevelopmental disease state exhibits neural circuit hyperconnectivity and hyperexcitability. Canonically, FMRP functions as an mRNA-binding translation suppressor, but recent findings have enormously expanded its proposed roles. Although connections between burgeoning FMRP functions remain unknown, recent advances have extended understanding of its involvement in RNA, channel, and protein binding that modulate calcium signaling, activity-dependent critical period development, and the excitation-inhibition (E/I) neural circuitry balance. In this review, we contextualize 3 years of FXS model research. Future directions extrapolated from recent advances focus on discovering links between FMRP roles to determine whether FMRP has a multitude of unrelated functions or whether combinatorial mechanisms can explain its multifaceted existence.
Keywords: Fragile X syndrome (FXS); activity-dependent critical period; autism spectrum disorder (ASD); synapse; translation regulation.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Weisz ED, et al. Deciphering discord: How Drosophila research has enhanced our understanding of the importance of FMRP in different spatial and temporal contexts. Exp. Neurol. 2015;274:14–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

