Inhibition of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 Attenuates Salt-Induced Hypertension and Kidney Injury in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats
- PMID: 28827472
- PMCID: PMC5599353
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09456
Inhibition of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 Attenuates Salt-Induced Hypertension and Kidney Injury in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats
Abstract
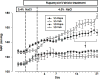
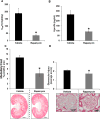
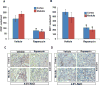
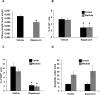
The goal of the present study was to explore the protective effects of mTORC1 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1) inhibition by rapamycin on salt-induced hypertension and kidney injury in Dahl salt-sensitive (SS) rats. We have previously demonstrated that H2O2 is elevated in the kidneys of SS rats. The present study showed a significant upregulation of renal mTORC1 activity in the SS rats fed a 4.0% NaCl for 3 days. In addition, renal interstitial infusion of H2O2 into salt-resistant Sprague Dawley rats for 3 days was also found to stimulate mTORC1 activity independent of a rise of arterial blood pressure. Together, these data indicate that the salt-induced increases of renal H2O2 in SS rats activated the mTORC1 pathway. Daily administration of rapamycin (IP, 1.5 mg/kg per day) for 21 days reduced salt-induced hypertension from 176.0±9.0 to 153.0±12.0 mm Hg in SS rats but had no effect on blood pressure salt sensitivity in Sprague Dawley treated rats. Compared with vehicle, rapamycin reduced albumin excretion rate in SS rats from 190.0±35.0 to 37.0±5.0 mg/d and reduced the renal infiltration of T lymphocytes (CD3+) and macrophages (ED1+) in the cortex and medulla. Renal hypertrophy and cell proliferation were also reduced in rapamycin-treated SS rats. We conclude that enhancement of intrarenal H2O2 with a 4.0% NaCl diet stimulates the mTORC1 pathway that is necessary for the full development of the salt-induced hypertension and kidney injury in the SS rat.
Keywords: arterial pressure; blood pressure; hypertension; rats, Sprague-Dawley.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

