Characterization of Monkeypox virus infection in African rope squirrels (Funisciurus sp.)
- PMID: 28827792
- PMCID: PMC5578676
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005809
Characterization of Monkeypox virus infection in African rope squirrels (Funisciurus sp.)
Abstract
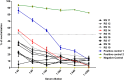
Monkeypox (MPX) is a zoonotic disease endemic in Central and West Africa and is caused by Monkeypox virus (MPXV), the most virulent Orthopoxvirus affecting humans since the eradication of Variola virus (VARV). Many aspects of the MPXV transmission cycle, including the natural host of the virus, remain unknown. African rope squirrels (Funisciurus spp.) are considered potential reservoirs of MPXV, as serosurveillance data in Central Africa has confirmed the circulation of the virus in these rodent species [1,2]. In order to understand the tissue tropism and clinical signs associated with infection with MPXV in these species, wild-caught rope squirrels were experimentally infected via intranasal and intradermal exposure with a recombinant MPXV strain from Central Africa engineered to express the luciferase gene. After infection, we monitored viral replication and shedding via in vivo bioluminescent imaging, viral culture and real time PCR. MPXV infection in African rope squirrels caused mortality and moderate to severe morbidity, with clinical signs including pox lesions in the skin, eyes, mouth and nose, dyspnea, and profuse nasal discharge. Both intranasal and intradermal exposures induced high levels of viremia, fast systemic spread, and long periods of viral shedding. Shedding and luminescence peaked at day 6 post infection and was still detectable after 15 days. Interestingly, one sentinel animal, housed in the same room but in a separate cage, also developed severe MPX disease and was euthanized. This study indicates that MPXV causes significant pathology in African rope squirrels and infected rope squirrels shed large quantities of virus, supporting their role as a potential source of MPXV transmission to humans and other animals in endemic MPX regions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


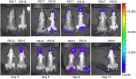




References
-
- Khodakevich L, Szczeniowski M, Manbu ma D, Jezek Z, Marennikova S, et al. (1987) The role of squirrels in sustaining monkeypox virus transmission. Trop Geogr Med 39: 115–122. - PubMed
-
- McCollum AM, Damon IK (2014) Human monkeypox. Clin Infect Dis 58: 260–267. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit703 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Damon IK (2011) Status of human monkeypox: clinical disease, epidemiology and research. Vaccine 29 Suppl 4: D54–59. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds MG, Carroll DS, Olson VA, Hughes C, Galley J, et al. (2010) A Silent Enzootic of an Orthopoxvirus in Ghana, West Africa: Evidence for Multi-Species Involvement in the Absence of Widespread Human Disease. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 82: 746–754. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0716 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

