Structure-activity relationships and molecular docking studies of chromene and chromene based azo chromophores: A novel series of potent antimicrobial and anticancer agents
- PMID: 28828001
- PMCID: PMC5547389
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2017-356
Structure-activity relationships and molecular docking studies of chromene and chromene based azo chromophores: A novel series of potent antimicrobial and anticancer agents
Abstract
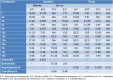
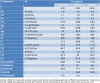
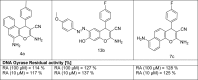
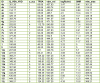
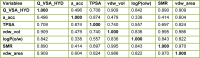
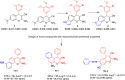
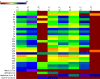
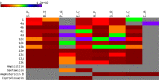
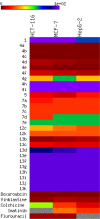
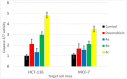
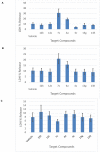
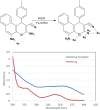
The design of novel materials with significant biological properties is a main target in drug design research. Chromene compounds represent an interesting medicinal scaffold in drug replacement systems. This report illustrates a successful synthesis and characterization of two novel series of chromene compounds using multi-component reactions. The synthesis of the first example of azo chromophores containing chromene moieties has also been established using the same methodology. The antimicrobial activity of the new molecules has been tested against seven human pathogens including two Gm+ve, two Gm-ve bacteria, and four fungi, and the results of the inhibition zones with minimum inhibitory concentrations were reported as compared to reference drugs. All the designed compounds showed significant potent antimicrobial activities, among of them, four potent compounds 4b, 4c, 13e, and 13i showed promising MIC from 0.007 to 3.9 µg/mL. In addition, antiproliferative analysis against three target cell lines was examined for the novel compounds. Compounds 4a, 4b, 4c, and 7c possessed significant antiproliferative activity against three cell lines with an IC50 of 0.3 to 2 µg/mL. Apoptotic analysis was performed for the most potent compounds via caspase enzyme activity assays as a potential mechanism for their antiproliferative effects. Finally, the computational 2D QSAR and docking simulations were accomplished for structure-activity relationship analyses.
Keywords: 2D QSAR and docking simulations; antitumor activity; biological applications; chromene azo dyes; chromene compounds.
Figures




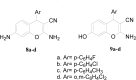




References
-
- Abd-El-Aziz AS, Afifi TH. Novel azo disperse dyes derived from aminothiophenes: Synthesis and UV–visible studies. Dyes and Pigments. 2006;70:8–17.
-
- Abd-El-Aziz AS, Alsaggaf AT, Okasha RM, Ahmed HEA, Bissessur R, Abdelghani AA, et al. Antimicrobial and antitumor screening of fluorescent 5,7-dihydroxy-4-propyl-2H-chromen-2-one derivatives with docking studies. Chemistry Select. 2016;1:5025–5033.
-
- Afifi TH. One-bath dyeing of polyester/wool blend using azodyes derived from 2-aminothiophenes. Adv Colour Sci Technol. 2003;6:63–72.
-
- Ahmed HEA, Abdel-Salam HA, Shaker MA. Synthesis, characterization, molecular modeling, and potential antimicrobial and anticancer activities of novel 2-aminoisoindoline-1,3-dione derivatives. Bioorg Chem. 2016;66:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Ali KA, Abdelhafez NAA, Ragab EA, Ibrahim AA, Amr AE. Design and synthesis of novel fused heterocycles using 4-chromanone as synthon. Russ J Gen Chem. 2015;85:2853–2860.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
