Recruitment maneuvers in acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 28828365
- PMCID: PMC5537118
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2017.07.09
Recruitment maneuvers in acute respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
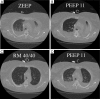
The rationale for the use of recruitment maneuvers (RMs) in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is to promote alveolar recruitment, leading to an increased end-expiratory lung volume and thus decreased ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI). RMs consists of a transient increase in transpulmonary pressure that can re-open previously collapsed alveoli. RMs represents a physiological response to lung aggression in different conditions by re-opening the collapsed part of the lung and decreasing lung oedema. This process can be accomplished through a variety of methods. The RM that has probably been used most commonly is sustained inflation, but recruitment can be achieved by a prolonged sigh, leading to a lesser increase in transpulmonary pressure for a longer period of time. This extended sigh seems to be more efficient, with less haemodynamic compromise. Knowledge of physiological determinants is crucial to selecting good levels of pressure and time required to perform an efficient and well-tolerated RM. Identifying ARDS patients who may benefit from RMs is a major issue, depending essentially on the amount of recruitable lung involved. In any case, however, RMs should be done at the early phase of ARDS.
Keywords: Recruitment maneuvers (RMs); acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); lung oedema; mechanical ventilation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Fan E, Del Sorbo L, Goligher EC, et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Society of Intensive Care Medicine/Society of Critical Care Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline: Mechanical Ventilation in Adult Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2017;195:1253-63. 10.1164/rccm.201703-0548ST - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
