Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP-1) Induction by Cocaine Is Post-Transcriptionally Regulated by miR-125b
- PMID: 28828398
- PMCID: PMC5562297
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0089-17.2017
Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP-1) Induction by Cocaine Is Post-Transcriptionally Regulated by miR-125b
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Dash et al., Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP-1) Induction by Cocaine Is Post-Transcriptionally Regulated by miR-125b (eNeuro July/August 2017, 4(4) e0089-17.2017 1-16 https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0089-17.2017).eNeuro. 2018 Apr 18;5(2):ENEURO.0115-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0115-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 29766043 Free PMC article.
Abstract
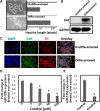
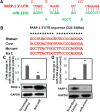
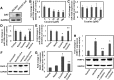
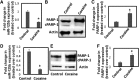
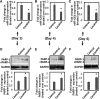
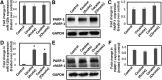
Cocaine exposure alters gene expression in the brain via methylation and acetylation of histones along with methylation of DNA. Recently, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) catalyzed PARylation has been reported as an important regulator of cocaine-mediated gene expression. In this study, we report that the cellular microRNA "miR-125b" plays a key role for cocaine-induced PARP-1 expression. Acute and chronic cocaine exposure resulted in the downregulation of miR-125b concurrent with upregulation of PARP-1 in dopaminergic neuronal cells and nucleus accumbens (NAc) of mice but not in the medial prefrontal cortex (PFC) or ventral tegmental area (VTA). In silico analysis predicted a binding site of miR-125b in a conserved 3'-untranslated region (3'UTR) of the PARP-1 mRNA. Knockdown and overexpression studies showed that miR-125b levels negatively correlate with PARP-1 protein expression. Luciferase reporter assay using a vector containing the 3'UTR of PARP-1 mRNA confirmed regulation of PARP-1 by miR-125b. Specific nucleotide mutations within the binding site abrogated miR-125b's regulatory effect on PARP-1 3'UTR. Finally, we established that downregulation of miR-125b and concurrent upregulation of PARP-1 is dependent on binding of cocaine to the dopamine transporter (DAT). Collectively, these results identify miR-125b as a post-transcriptional regulator of PARP-1 expression and establish a novel mechanism underlying the molecular effects of cocaine action.
Keywords: PARP-1; PARylation; cocaine; miRNA; post-transcriptional regulation.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DA036420/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DA042111/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA008227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DA030896/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA007359/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR000447/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA014133/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD008149/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DA024558/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DA024558/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007586/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DA021471/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI122960/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DA033892/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 RR024978/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI110527/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007593/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR026140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DA037779/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DA042111/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
