Intrathecal Resiniferatoxin Modulates TRPV1 in DRG Neurons and Reduces TNF-Induced Pain-Related Behavior
- PMID: 28831207
- PMCID: PMC5558708
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/2786427
Intrathecal Resiniferatoxin Modulates TRPV1 in DRG Neurons and Reduces TNF-Induced Pain-Related Behavior
Abstract
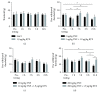
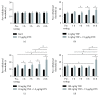
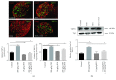
Transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) is a nonselective cation channel, predominantly expressed in sensory neurons. TRPV1 is known to play an important role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and neuropathic pain states. Previous studies suggest interactions between tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-) alpha and TRPV1, resulting in a modulation of ion channel function and protein expression in sensory neurons. We examined the effect of intrathecal administration of the ultrapotent TRPV1 agonist resiniferatoxin (RTX) on TNF-induced pain-associated behavior of rats using von Frey and hot plate behavioral testing. Intrathecal injection of TNF induces mechanical allodynia (2 and 20 ng/kg) and thermal hyperalgesia (200 ng) 24 h after administration. The additional intrathecal administration of RTX (1.9 μg/kg) alleviates TNF-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia 24 h after injection. In addition, TNF increases the TRPV1 protein level and number of TRPV1-expressing neurons. Both effects could be abolished by the administration of RTX. These results suggest that the involvement of TRPV1 in TNF-induced pain offers new TRPV1-based experimental therapeutic approaches and demonstrates the analgesic potential of RTX in inflammatory pain diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Ohtori S., Takahashi K., Moriya H., Myers R. R. TNF-alpha and TNF-alpha receptor type 1 upregulation in glia and neurons after peripheral nerve injury: studies in murine DRG and spinal cord. Spine. 2004;29:1082–1088. - PubMed
-
- Murphy G. M., Jr., Lee Y. L., Jia X. C., et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and basic fibroblast growth factor decrease glial fibrillary acidic protein and its encoding mRNA in astrocyte cultures and glioblastoma cells. Journal of Neurochemistry. 1995;65:2716–2724. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65062716.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schafers M., Lee D. H., Brors D., Yaksh T. L., Sorkin L. S. Increased sensitivity of injured and adjacent uninjured rat primary sensory neurons to exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha after spinal nerve ligation. The Journal of Neuroscience : The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2003;23:3028–3038. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schafers M., Sorkin L. S., Geis C., Shubayev V. I. Spinal nerve ligation induces transient upregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptors 1 and 2 in injured and adjacent uninjured dorsal root ganglia in the rat. Neuroscience Letters. 2003;347:179–182. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

