Cuticular surface damage of Ascaridia galli adult worms treated with Veitchia merrillii betel nuts extract in vitro
- PMID: 28831213
- PMCID: PMC5553138
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2017.732-737
Cuticular surface damage of Ascaridia galli adult worms treated with Veitchia merrillii betel nuts extract in vitro
Abstract
Aim: The objective of this research was to in vitro evaluate the cuticular surface damage of Ascaridia galli adult worms treated with ethanolic extract of betel nuts Veitchia merrillii.
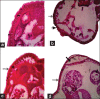
Materials and methods: Phytochemical screening was done using FeCl3, Wagner and Dragendorff reagents, NaOH, MgHCl, and Liebermann-Burchard reaction test. Amount of 16 worms were segregated into four groups with three replicates. Four worms of each group submerged into phosphate buffered saline, 25 mg/ml, and 75 mg/ml crude ethanolic extract of V. merrillii, and 15 mg/ml albendazole. The effect of these extract was observed 40 h after incubation as soon as worms death. The worms were sectioned transversally and were explored for any cuticular histopathological changes in their body surface under microscope.
Results: We found that the ethanolic extract of V. merrillii betel nuts contains tannins, alkaloids, flavonoids, triterpenoids, and saponins. The ethanolic extract of betel nuts V. merrillii induces surface alterations caused cuticular damage of A. galli adult worms.
Conclusion: We concluded that ethanolic extract of betel nuts V. merrillii possess anthelmintic activity caused cuticular damage of A. galli adult worms.
Keywords: Ascaridia galli; Veitchia merrillii; anthelmintics; cuticle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro and in silico study on the seeds of Veitchia merrillii on trematode worms.Vet World. 2024 Jun;17(6):1336-1347. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.1336-1347. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 39077451 Free PMC article.
-
Anthelmintic effects of citrus peels ethanolic extracts against Ascaridia galli.Vet Parasitol. 2012 Aug 13;188(1-2):78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.03.003. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Vet Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22463876 Clinical Trial.
-
In vitro anthelmintic activity of Phyllanthus niruri Linn., Andrographis paniculata, Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb., and Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb. ethanol extracts on the motility and cuticle damage of Ascaridia galli.Vet World. 2024 Nov;17(11):2488-2496. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.2488-2496. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 39829662 Free PMC article.
-
Parasiticidal and brine shrimp cytotoxicity potential of crude methanolic extract of rind of Punica granatum Linn against round worms and tape worms.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015 May;28(3):959-62. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 26004729
-
[Anthelmintic activity of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Morinda citrifolia fruit on Ascaridia galli].Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2009 Oct-Dec;18(4):32-6. doi: 10.4322/rbpv.01804006. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2009. PMID: 20040206 Portuguese.
Cited by
-
Angiogenesis activity of Jatropha curcas L. latex in cream formulation on wound healing in mice.Vet World. 2018 Jul;11(7):939-943. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2018.939-943. Epub 2018 Jul 15. Vet World. 2018. PMID: 30147263 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of Jatropha curcas Linn. latex in cream formulation on CD68 expression in mice skin wound.Vet World. 2018 Feb;11(2):99-103. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2018.99-103. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Vet World. 2018. PMID: 29657387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hassanain M.A, Rahman E.H.A, Khalil F.A.M. New scanning electron microscopy look of Ascaridia galli (Schrank 1788) adult worm and its biological control. Res. J. Parasitol. 2009;4:1–11.
-
- Begum S, Mostofa M, Alam A.K.M, Tanjim M, Ali A.A.M, Islam M.N, Das S. Prevalence of ascariasis and comparitave efficacy of pinapple leaves extract with patent drug piperazine against ascariasis of poultry at five villages under mymensingh district. Int. J. Biol. Res. 2010;1(5):41–44.
-
- Saha B.K, Abdullah-Al-Hasan M.D, Rahman M.A, Hassan M.D.M, Begum N. Comparative eefficacy of neem leaves extract and levamisole against ascariasis in chicken. Int. J. Nat. Soc. Sci. 2015;2:43–48.
-
- Kaufmann F, Das G, Sohnrey B, Gauly M. Helminth infections in laying hens kept in organic free range systems in Germany. Livest. Sci. 2011;141:182–187.
-
- Abdelqader A, Gauly M, Wollny C.B, Abo-Shehdada M.N. Prevalence and burden of gastro-intestinal helminths among local chickens in northern Jordan. Prev. Vet. Med. 2008;85:17–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
