Development of a novel microemulsion for oral absorption enhancement of all-trans retinoic acid
- PMID: 28831254
- PMCID: PMC5548273
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S142503
Development of a novel microemulsion for oral absorption enhancement of all-trans retinoic acid
Abstract
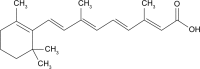
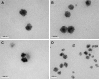
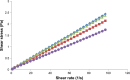
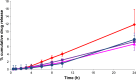
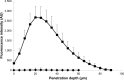
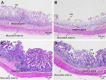
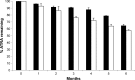
This study was aimed to develop a novel microemulsion that contained oleth-5 as a surfactant to enhance the oral absorption of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA). The prepared microemulsion was evaluated for its particle size, shape, zeta potential, in vitro release, in vitro intestinal absorption, intestinal membrane cytotoxicity and stability. The obtained microemulsion was spherical in shape with a particle size of <200 nm and a negative surface charge. The in vitro release of the ATRA-loaded microemulsion was best fit with the zero-order model. This microemulsion significantly improved the intestinal absorption of ATRA. Confocal laser scanning microscopy analysis using a fluorescent dye-loaded microemulsion also confirmed the intestinal absorption result. The intestinal membrane cytotoxicity of the ATRA-loaded microemulsion did not differ from an edible oil (fish oil). Stability testing showed that the ATRA-loaded microemulsion was more stable at 25°C than 40°C.
Keywords: all-trans retinoic acid; fish oil; microemulsion; oleth-5; oral absorption enhancement.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Adamson PC. All-trans-retinoic acid pharmacology and its impact on the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncologist. 1996;1(5):305–314. - PubMed
-
- Muindi JR, Frankel SR, Huselton C, et al. Clinical pharmacology of oral all-trans retinoic acid in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Res. 1992;52(8):2138–2142. - PubMed
-
- Qi ZH, Shieh WJ. Aqueous media for effective delivery of tretinoin. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2002;44(1):133–136.
-
- Li Z, Han X, Zhai Y, et al. Critical determinant of intestinal permeability and oral bioavailabilityof pegylated all trans-retinoic acid prodrug-based nanomicelles: chain length of poly (ethylene glycol) corona. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;130:133–140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

