PALOMA-3: Phase III Trial of Fulvestrant With or Without Palbociclib in Premenopausal and Postmenopausal Women With Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer That Progressed on Prior Endocrine Therapy-Safety and Efficacy in Asian Patients
- PMID: 28831437
- PMCID: PMC5560465
- DOI: 10.1200/JGO.2016.008318
PALOMA-3: Phase III Trial of Fulvestrant With or Without Palbociclib in Premenopausal and Postmenopausal Women With Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer That Progressed on Prior Endocrine Therapy-Safety and Efficacy in Asian Patients
Abstract
Purpose: To assess efficacy and safety of palbociclib plus fulvestrant in Asians with endocrine therapy-resistant metastatic breast cancer.
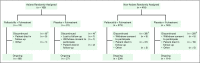
Patients and methods: The Palbociclib Ongoing Trials in the Management of Breast Cancer 3 (PALOMA-3) trial, a double-blind phase III study, included 521 patients with hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative metastatic breast cancer with disease progression on endocrine therapy. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) were assessed on study treatment and at the end of treatment.
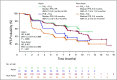
Results: This preplanned subgroup analysis of the PALOMA-3 study included premenopausal and postmenopausal Asians taking palbociclib plus fulvestrant (n = 71) or placebo plus fulvestrant (n = 31). Palbociclib plus fulvestrant improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared with fulvestrant alone. Median PFS was not reached with palbociclib plus fulvestrant (95% CI, 9.2 months to not reached) but was 5.8 months with placebo plus fulvestrant (95% CI, 3.5 to 9.2 months; hazard ratio, 0.485; 95% CI, 0.270 to 0.869; P = .0065). The most common all-cause grade 3 or 4 adverse events in the palbociclib arm were neutropenia (92%) and leukopenia (29%); febrile neutropenia occurred in 4.1% of patients. Within-patient mean trough concentration comparisons across subgroups indicated similar palbociclib exposure between Asians and non-Asians. Global quality of life was maintained; no statistically significant changes from baseline were observed for patient-reported outcome scores with palbociclib plus fulvestrant.
Conclusion: This is the first report, to our knowledge, showing that palbociclib plus fulvestrant improves PFS in asian patients. Palbociclib plus fulvestrant was well tolerated in this study.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/jco/site/ifc. Hiroji IwataConsulting or Advisory Role: Chugai Pharma, Eisai, AstraZenecaSeock-Ah ImConsulting or Advisory Role: AstraZeneca, Novartis, Roche, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Research Funding: AstraZenecaNorikazu MasudaHonoraria: Chugai Pharma, AstraZeneca Research Funding: Chugai Pharma (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Eli Lilly (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Kyowa-Kirin (Inst)Young-Hyuck ImNo relationship to discloseKenichi InoueResearch Funding: Pfizer (Inst), Eli Lilly (Inst), Chugai Pharma, Daiichi-Sankyo (Inst), Taiho Pharmaceutical (Inst), MSD (Inst), Parexel (Puma) (Inst)Yoshiaki RaiNo relationship to discloseRikiya NakamuraNo relationship to discloseJee Hyun KimNo relationship to discloseJustin T. HoffmanEmployment: Pfizer Stock or Other Ownership: Pfizer Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: PfizerKe ZhangEmployment: Pfizer (former employer), Janssen Research and Development (current employer) Stock or Other Ownership: PfizerCarla GiorgettiEmployment: Pfizer Stock or Other Ownership: PfizerShrividya IyerEmployment: Pfizer Stock or Other Ownership: PfizerPatrick T. SchnellEmployment: Pfizer Stock or Other Ownership: PfizerCynthia Huang BartlettEmployment: Pfizer Stock or Other Ownership: PfizerJungsil RoNo relationship to disclose
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- American Cancer Society Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2015-2016. http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@research/documents/document/ac...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

