Spectral EMG Changes in Cervical Dystonia Patients and the Influence of Botulinum Toxin Treatment
- PMID: 28832550
- PMCID: PMC5618189
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins9090256
Spectral EMG Changes in Cervical Dystonia Patients and the Influence of Botulinum Toxin Treatment
Abstract
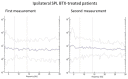
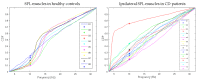
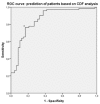
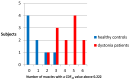
Botulinum toxin (BoNT) injections in the dystonic muscles is the preferred treatment for Cervical Dystonia (CD), but the proper identification of the dystonic muscles remains a challenge. Previous studies showed decreased 8-14 Hz autospectral power in the electromyography (EMG) of splenius muscles in CD patients. Cumulative distribution functions (CDF's) of dystonic muscles showed increased CDF10 values, representing increased autospectral powers between 3 and 10 Hz, relative to power between 3 and 32 Hz. In this study, we evaluated both methods and investigated the effects of botulinum toxin. Intramuscular EMG recordings were obtained from the splenius, semispinalis, and sternocleidomastoid muscles during standardized isometric tasks in 4 BoNT-naïve CD patients, 12 BoNT-treated patients, and 8 healthy controls. BoNT-treated patients were measured 4-7 weeks after their last BoNT injections and again after 11-15 weeks. We found significantly decreased 8-14 Hz autospectral power in splenius muscles, but not in the semispinalis and sternocleidomastoid muscles of CD patients when compared to healthy controls. CDF10 analysis was superior in demonstrating subtle autospectral changes, and showed increased CDF10 values in all studied muscles of CD patients. These results did not change significantly after BoNT injections. Further studies are needed to investigate the origin of these autospectral changes in dystonia patients, and to assess their potential in muscle selection for BoNT treatment.
Keywords: EMG; autospectral analysis; botulinum toxin; cervical dystonia; muscle selection.
Conflict of interest statement
M.T: Funds: Nuts-Ohra, Princes Beatrix Muscle fund, Gossweiler foundation, Science Foundation Dystonia Society, Funds Mental Health, Phelps Foundation, Beatrix Children Hospital Fund, Healthy Aging Fund UMCG. M.T. received unrestricted grants from Actelion, Merz, Ipsen, Allergan Pharmaceutics & Medtronic and a Honorarium from the Merz expert meeting in Paris, January 2016. These sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results. J.K.: Funds: Princes Beatrix Muscle fund. The AMC movement disorder group received unrestricted educational and research grants from Ipsen and Allergan. These sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
EMG coherence and spectral analysis in cervical dystonia: discriminative tools to identify dystonic muscles?J Neurol Sci. 2014 Dec 15;347(1-2):167-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2014.09.041. Epub 2014 Oct 2. J Neurol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25305713
-
Dystonic neck muscles show a shift in relative autospectral power during isometric contractions.Clin Neurophysiol. 2017 Oct;128(10):1937-1945. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2017.06.258. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28826024
-
The clinical utility of botulinum toxin injections targeted at the motor endplate zone in cervical dystonia.Eur J Neurol. 2014 Dec;21(12):1486-e98. doi: 10.1111/ene.12517. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Eur J Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25060697
-
[Treatment of focal dystonia with botulinum toxin A].Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2001;113 Suppl 4:6-10. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2001. PMID: 15506045 Review. German.
-
A methodological approach for botulinum neurotoxin injections to the longus colli muscle in dystonic anterocollis: A case series of 4 patients and a literature review.J Clin Neurosci. 2020 Oct;80:188-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2020.08.025. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33099344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improving the Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin for Cervical Dystonia: A Scoping Review.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;15(6):391. doi: 10.3390/toxins15060391. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37368692 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Ultrasound for the Personalized Botulinum Toxin Treatment of Cervical Dystonia.Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 20;13(5):365. doi: 10.3390/toxins13050365. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34065541 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cordivari C., Misra V.P., Vincent A., Catania S., Bhatia K.P., Lees A.J. Secondary nonresponsiveness to botulinum toxin A in cervical dystonia: The role of electromyogram-guided injections, botulinum toxin A antibody assay, and the extensor digitorum brevis test. Mov. Disord. 2006;21:1737–1741. doi: 10.1002/mds.21051. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

