High-density 80 K SNP array is a powerful tool for genotyping G. hirsutum accessions and genome analysis
- PMID: 28835210
- PMCID: PMC5569476
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-4062-2
High-density 80 K SNP array is a powerful tool for genotyping G. hirsutum accessions and genome analysis
Abstract
Background: High-throughput genotyping platforms play important roles in plant genomic studies. Cotton (Gossypium spp.) is the world's important natural textile fiber and oil crop. Upland cotton accounts for more than 90% of the world's cotton production, however, modern upland cotton cultivars have narrow genetic diversity. The amounts of genomic sequencing and re-sequencing data released make it possible to develop a high-quality single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array for intraspecific genotyping detection in cotton.
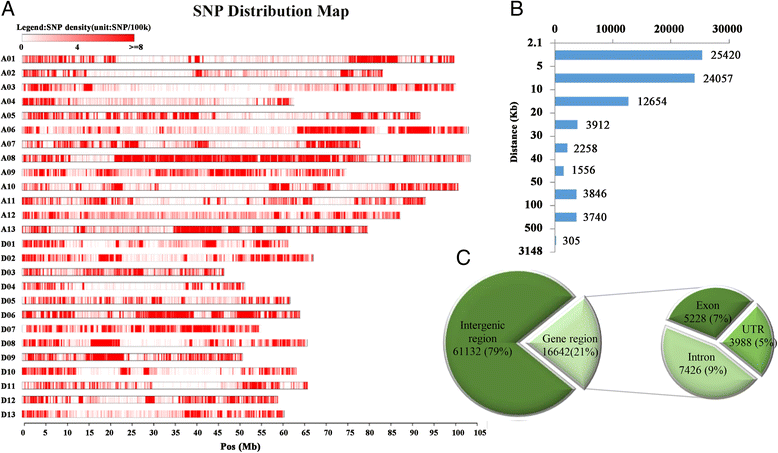
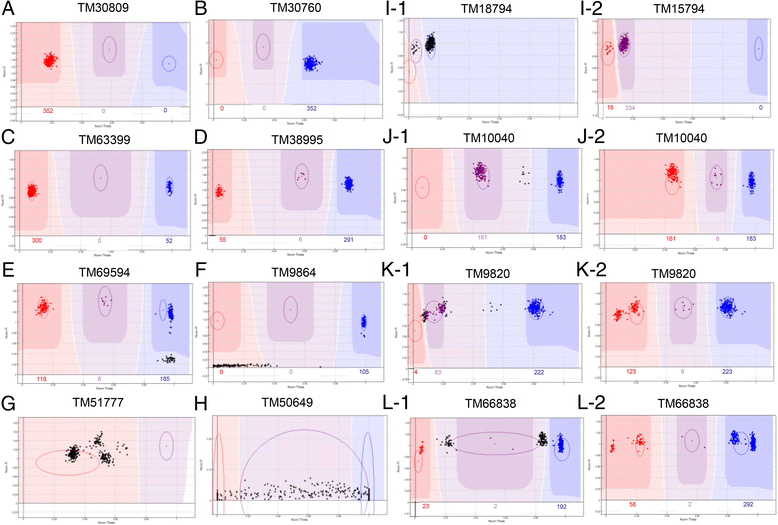
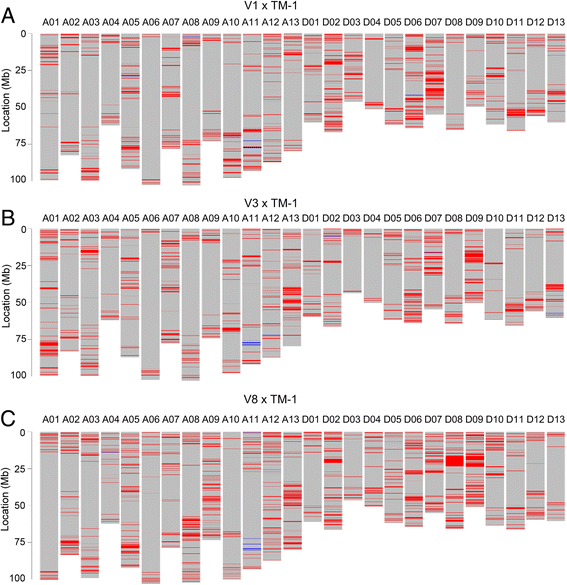
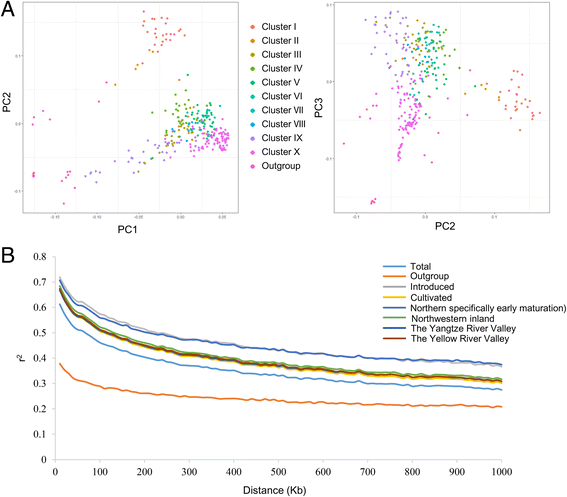
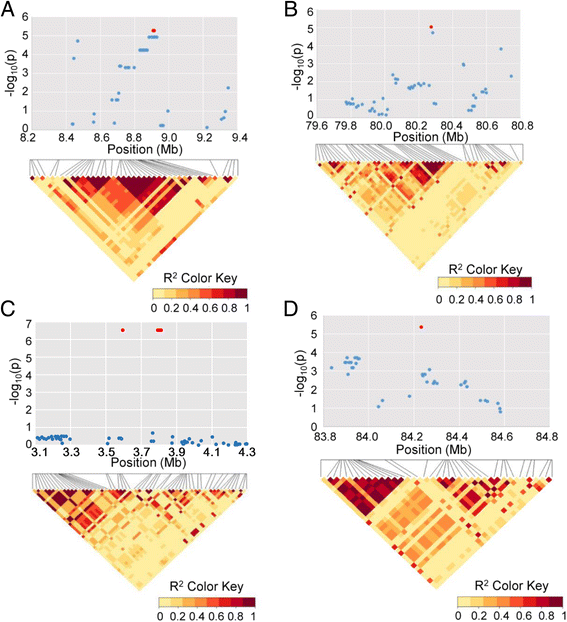
Results: Here we report a high-throughput CottonSNP80K array and its utilization in genotyping detection in different cotton accessions. 82,259 SNP markers were selected from the re-sequencing data of 100 cotton cultivars and used to produce the array on the Illumina Infinium platform. 77,774 SNP loci (94.55%) were successfully synthesized on the array. Of them, 77,252 (99.33%) had call rates of >95% in 352 cotton accessions and 59,502 (76.51%) were polymorphic loci. Application tests using 22 cotton accessions with parent/F1 combinations or with similar genetic backgrounds showed that CottonSNP80K array had high genotyping accuracy, good repeatability, and wide applicability. Phylogenetic analysis of 312 cotton cultivars and landraces with wide geographical distribution showed that they could be classified into ten groups, irrelevant of their origins. We found that the different landraces were clustered in different subgroups, indicating that these landraces were major contributors to the development of different breeding populations of modern G. hirsutum cultivars in China. We integrated a total of 54,588 SNPs (MAFs >0.05) associated with 10 salt stress traits into 288 G. hirsutum accessions for genome-wide association studies (GWAS), and eight significant SNPs associated with three salt stress traits were detected.
Conclusions: We developed CottonSNP80K array with high polymorphism to distinguish upland cotton accessions. Diverse application tests indicated that the CottonSNP80K play important roles in germplasm genotyping, variety verification, functional genomics studies, and molecular breeding in cotton.
Keywords: Array; Genome-wide association studies (GWAS); Genotyping identification; Molecular breeding; Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP); Upland cotton.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
A total of 352 cotton materials, including 332
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declared that they had no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Bowman DT, May OL, Calhoun DS. Genetic base of upland cotton cultivars released between 1970 and 1990. Crop Sci. 1996;36(3):577–81.
-
- Hulse-Kemp AM, Ashrafi H, Stoffel K, Zheng X, Saski CA, Scheffler BE, Fang DD, et al. BAC-end sequence-based SNP mining in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium) utilizing resequencing data, phylogenetic inferences, and perspectives for genetic mapping. Genes Genomes Genetics. 2015;5(6):1095–1105. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

