Is Staphylococcus lugdunensis Significant in Clinical Samples?
- PMID: 28835477
- PMCID: PMC5654899
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00846-17
Is Staphylococcus lugdunensis Significant in Clinical Samples?
Abstract
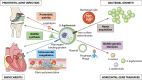
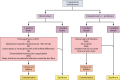
The implication of coagulase-negative staphylococci in human diseases is a major issue, particularly in hospital settings wherein these species often act as opportunistic pathogens. In addition, some coagulase-negative staphylococci such as S. lugdunensis have emerged as pathogenic bacteria, implicated in severe infections, particularly, osteoarticular infections, foreign-body-associated infections, bacteremia, and endocarditis. In vitro studies have shown the presence of several putative virulence factors such as adhesion factors, biofilm production, and proteolytic factors that might explain clinical manifestations. Taken together, the clinical and microbiological data might change the way clinicians and microbiologists look at S. lugdunensis in clinical samples.
Keywords: Staphylococcus lugdunensis; biofilm; endocarditis; osteoarticular infections; protease; virulence.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Argemi X, Riegel P, Lavigne T, Lefebvre N, Grandpré N, Hansmann Y, Jaulhac B, Prévost G, Schramm F. 2015. Implementation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry in routine clinical laboratories improves identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci and reveals the pathogenic role of Staphylococcus lugdunensis. J Clin Microbiol 53:2030–2036. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00177-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Argemi X, Prévost G, Riegel P, Keller D, Meyer N, Baldeyrou M, Douiri N, Lefebvre N, Meghit K, Ronde Oustau C, Christmann D, Cianférani S, Strub JM, Hansmann Y. 2017. VISLISI trial, a prospective clinical study allowing identification of a new metalloprotease and putative virulence factor from Staphylococcus lugdunensis. Clin Microbiol Infect 23:334.e1–334.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.12.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

