Postdose 3 G1 serum neutralizing antibody as correlate of protection for pentavalent rotavirus vaccine
- PMID: 28836489
- PMCID: PMC5647971
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1356522
Postdose 3 G1 serum neutralizing antibody as correlate of protection for pentavalent rotavirus vaccine
Abstract
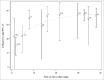
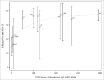
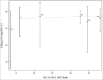
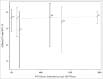
Although clinical trials of the pentavalent rotavirus vaccine (RotaTeq®, RV5) have demonstrated efficacy against RV gastroenteritis (RGE) in low and high-income settings, a clear correlate of protection or a measure of immune response that could predict efficacy has yet to be identified. This is the first time that immunogenicity data with both serum neutralized antibody (SNA) titers and anti-RV IgA titers from several clinical efficacy trials were pooled to provide a unique context for evaluating the correlation between immunogenicity and RGE risk or efficacy of RV5. The correlation between immunogenicity and RGE risk is evaluated with data at the individual subject level. The analyses show that higher Postdose 3 (PD3) G1 SNA titers are associated with lower odds of contracting any RGE. The correlation between immunogenicity and efficacy is assessed using aggregated population level data, which shows higher efficacy associated with higher PD3 G1 SNA geometric mean titer (GMT) ratio (between RV5 and placebo) and PD3 serum anti-RV IgA GMT ratio. Among high-income countries, efficacy plateaus over the range of PD3 G1 SNA GMT ratios and PD3 serum anti-RV IgA GMT ratios. From both individual- and population-level analyses, PD3 G1 SNA titers correlated most closely with the RGE risk or efficacy for RV5.
Keywords: correlation of protection; geometric mean titer (GMT); immunogenicity; pentavalent rotavirus vaccine (RV5); rotavirus gastroenteritis (RGE).
Figures

References
-
- Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, Parashar UD, World Health Organization–Coordinated Global Rotavirus Surveillance Network . Global, regional, and national estimates of rotavirus mortality in children <5 years of age, 2000–2013. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(Suppl 2):S96-S105. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ1013. PMID:27059362 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kapikian AZ, et al. Rotavirus. In: Kripe DM, editor(s). Fields virology. Vol 2 4th ed Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. p. 1787-825.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
