Botulinum Toxin for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
- PMID: 28837075
- PMCID: PMC5618193
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins9090260
Botulinum Toxin for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
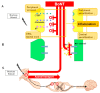
Botulinum toxin (BoNT) has been used as a treatment for excessive muscle stiffness, spasticity, and dystonia. BoNT for approximately 40 years, and has recently been used to treat various types of neuropathic pain. The mechanism by which BoNT acts on neuropathic pain involves inhibiting the release of inflammatory mediators and peripheral neurotransmitters from sensory nerves. Recent journals have demonstrated that BoNT is effective for neuropathic pain, such as postherpetic neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, and peripheral neuralgia. The purpose of this review is to summarize the experimental and clinical evidence of the mechanism by which BoNT acts on various types of neuropathic pain and describe why BoNT can be applied as treatment. The PubMed database was searched from 1988 to May 2017. Recent studies have demonstrated that BoNT injections are effective treatments for post-herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, trigeminal neuralgia, and intractable neuropathic pain, such as poststroke pain and spinal cord injury.
Keywords: botulinum toxin; neuropathic pain; neuropathic pain treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

