Heterologous Expression, Purification and Immunoreactivity of the Antigen 5 from Polybia paulista Wasp Venom
- PMID: 28837089
- PMCID: PMC5618192
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins9090259
Heterologous Expression, Purification and Immunoreactivity of the Antigen 5 from Polybia paulista Wasp Venom
Abstract
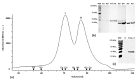
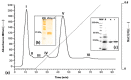
Polybia paulista (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) is responsible for a high number of sting accidents and anaphylaxis events in Southeast Brazil, Argentina and Paraguay. The specific detection of allergy to the venom of this wasp is often hampered by the lack of recombinant allergens currently available for molecular diagnosis. Antigen 5 (~23 kDa) from P. paulista venom (Poly p 5) is a highly abundant and glycosylated allergenic protein that could be used for development of component-resolved diagnosis (CRD). Here, we describe the cloning and heterologous expression of the antigen 5 (rPoly p 5) from P. paulista venom using the eukaryotic system Pichia pastoris. The expression as a secreted protein yielded high levels of soluble rPoly p 5. The recombinant allergen was further purified to homogeneity (99%) using a two-step chromatographic procedure. Simultaneously, the native form of the allergen (nPoly p 5) was purified from the wasp venom by Ion exchange chromatography. The rPoly p 5 and nPoly p 5 were then submitted to a comparative analysis of IgE-mediated immunodetection using sera from patients previously diagnosed with sensitization to wasp venoms. Both rPoly p 5 and nPoly p 5 were recognized by specific IgE (sIgE) in the sera of the allergic individuals. The high levels of identity found between nPoly p 5 and rPoly p 5 by the alignment of its primary sequences as well as by 3-D models support the results obtained in the immunoblot. Overall, we showed that P. pastoris is a suitable system for production of soluble rPoly p 5 and that the recombinant allergen represents a potential candidate for molecular diagnosis of P.paulista venom allergy.
Keywords: Polybia paulista; allergy; antigen 5; diagnosis; heterologous expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

