Radiologic Features of Small Pulmonary Nodules and Lung Cancer Risk in the National Lung Screening Trial: A Nested Case-Control Study
- PMID: 28837413
- PMCID: PMC5738292
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2017161458
Radiologic Features of Small Pulmonary Nodules and Lung Cancer Risk in the National Lung Screening Trial: A Nested Case-Control Study
Abstract
Purpose To extract radiologic features from small pulmonary nodules (SPNs) that did not meet the original criteria for a positive screening test and identify features associated with lung cancer risk by using data and images from the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST). Materials and Methods Radiologic features in SPNs in baseline low-dose computed tomography (CT) screening studies that did not meet NLST criteria to be considered a positive screening examination were extracted. SPNs were identified for 73 incident case patients who were given a diagnosis of lung cancer at either the first or second follow-up screening study and for 157 control subjects who had undergone three consecutive negative screening studies. Multivariable logistic regression was used to assess the association between radiologic features and lung cancer risk. All statistical tests were two sided. Results Nine features were significantly different between case patients and control subjects. Backward elimination followed by bootstrap resampling identified a reduced model of highly informative radiologic features with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.932 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.88, 0.96), a specificity of 92.38% (95% CI: 52.22%, 84.91%), and a sensitivity of 76.55% (95% CI: 87.50%, 95.35%) that included total emphysema score (odds ratio [OR] = 1.71; 95% CI: 1.39, 2.01), attachment to vessel (OR = 2.41; 95% CI: 0.99, 5.81), nodule location (OR = 3.25; 95% CI: 1.09, 8.55), border definition (OR = 7.56; 95% CI: 1.89, 30.8), and concavity (OR = 2.58; 95% CI: 0.89, 5.64). Conclusion A set of clinically relevant radiologic features were identified that that can be easily scored in the clinical setting and may be of use to determine lung cancer risk among participants with SPNs. © RSNA, 2017 Online supplemental material is available for this article.
Figures
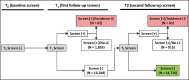
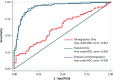
Comment in
-
Radiologic features of small pulmonary nodules detected in initially negative screening CT examinations: a step towards personalized screening strategies?Ann Transl Med. 2018 Nov;6(Suppl 1):S51. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.10.14. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30613626 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- MacMahon H, Austin JH, Gamsu G, et al. . Guidelines for management of small pulmonary nodules detected on CT scans: a statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2005;237(2):395–400. - PubMed
-
- Callister ME, Baldwin DR, Akram AR, et al. . British Thoracic Society guidelines for the investigation and management of pulmonary nodules. Thorax 2015;70(Suppl 2):ii1–ii54. [Published correction appears in Thorax 2015;70(12):1188.] - PubMed
-
- Benjamin MS, Drucker EA, McLoud TC, Shepard JA. Small pulmonary nodules: detection at chest CT and outcome. Radiology 2003;226(2):489–493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

