Human neutrophil elastase mediates fibrinolysis shutdown through competitive degradation of plasminogen and generation of angiostatin
- PMID: 28837538
- PMCID: PMC5767103
- DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001685
Human neutrophil elastase mediates fibrinolysis shutdown through competitive degradation of plasminogen and generation of angiostatin
Abstract
Background: A subset of trauma patients undergo fibrinolysis shutdown rather than pathologic hyperfibrinolysis, contributing to organ failure. The molecular basis for fibrinolysis shutdown in trauma is incompletely understood. Elastase released from primed/activated human neutrophils (HNE) has historically been described as fibrin(ogen)olytic. However, HNE can also degrade plasminogen (PLG) to angiostatin (ANG), retaining the kringle domains but not the proteolytic function, and could thereby compete for generation of active plasmin by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). We hypothesized that HNE can drive fibrinolysis shutdown rather than fibrinolysis.
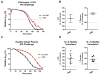
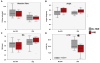
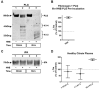
Methods: Turbidometry was performed using light scatter (λ = 620 nm) in a purified fibrinogen + PLG system and in healthy citrate plasma clotted with Ca/thrombin ± tPA, ±HNE, and ±ANG to evaluate HNE effects on fibrinolysis, quantified by time to transition midpoint (Tm). ΔTm from control is reported as percent of control ±95% CI. Purified HNE coincubated with PLG or tPA was analyzed by western blot to identify cleavage products. Exogenous HNE was mixed ex vivo with healthy volunteer blood (n = 7) and used in TEG ± tPA to evaluate effects on fibrinolysis.
Results: HNE did not cause measurable fibrinolysis on fibrin clots, clotted plasma, or whole blood as assessed by turbidometry or TEG in the absence of tPA. Upon tPA treatment, all three methods of evaluating fibrinolysis showed delays and decreases in fibrinolysis caused by HNE relative to control: fibrin clot turbidometry ΔTm = 110.7% (CI 105.0-116.5%), clotted citrate plasma (n = 6 healthy volunteers) ΔTm = 126.1% (CI 110.4-141.8%), and whole blood native TEG (n = 7 healthy volunteers) with ΔLY30 = 28% (p = 0.043). Western blot analysis of HNE-PLG co-incubation confirmed that HNE generates angiostatin K1-3, and plasma turbidity assays treated with angiostatin K1-3 delayed fibrinolysis.
Conclusion: HNE degrades PLG and generates angiostatin K1-3, which predominates over HNE cleavage of fibrin(ogen). These findings suggest that neutrophil release of elastase may underlie trauma-induced fibrinolytic shutdown.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest are reported.
Figures

References
-
- Moore HB, Moore EE, Gonzalez E, Chapman MP, Chin TL, Silliman CC, Banerjee A, Sauaia A. Hyperfibrinolysis, physiologic fibrinolysis, and fibrinolysis shutdown: the spectrum of postinjury fibrinolysis and relevance to antifibrinolytic therapy. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014;77(6):811–7. discussion -7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chapman MP, Moore EE, Moore HB, Gonzalez E, Gamboni F, Chandler JG, Mitra S, Ghasabyan A, Chin TL, Sauaia A, et al. Overwhelming tPA release, not PAI-1 degradation, is responsible for hyperfibrinolysis in severely injured trauma patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2016;80(1):16–23. discussion -5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cardenas JC, Matijevic N, Baer LA, Holcomb JB, Cotton BA, Wade CE. Elevated tissue plasminogen activator and reduced plasminogen activator inhibitor promote hyperfibrinolysis in trauma patients. Shock. 2014;41(6):514–21. - PubMed
-
- Moore HB, Moore EE, Chapman MP, Gonzalez E, Slaughter AL, Morton AP, D'Alessandro A, Hansen KC, Sauaia A, Banerjee A, et al. Viscoelastic measurements of platelet function, not fibrinogen function, predicts sensitivity to tissue-type plasminogen activator in trauma patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(10):1878–87. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

