Determinants of user acceptance of a specific social platform for older adults: An empirical examination of user interface characteristics and behavioral intention
- PMID: 28837566
- PMCID: PMC5570369
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180102
Determinants of user acceptance of a specific social platform for older adults: An empirical examination of user interface characteristics and behavioral intention
Abstract
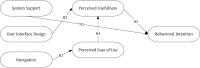
The use of the Internet and social applications has many benefits for the elderly, but numerous investigations have shown that the elderly do not perceive online social networks as a friendly social environment. Therefore, TreeIt, a social application specifically designed for the elderly, was developed for this study. In the TreeIt application, seven mechanisms promoting social interaction were designed to allow older adults to use social networking sites (SNSs) to increase social connection, maintain the intensity of social connections and strengthen social experience. This study's main objective was to investigate how user interface design affects older people's intention and attitude related to using SNSs. Fourteen user interface evaluation heuristics proposed by Zhang et al. were adopted as the criteria to assess user interface usability and further grouped into three categories: system support, user interface design and navigation. The technology acceptance model was adopted to assess older people's intention and attitude related to using SNSs. One hundred and one elderly persons were enrolled in this study as subjects, and the results showed that all of the hypotheses proposed in this study were valid: system support and perceived usefulness had a significant effect on behavioral intention; user interface design and perceived ease of use were positively correlated with perceived usefulness; and navigation exerted an influence on perceived ease of use. The results of this study are valuable for the future development of social applications for the elderly.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures








References
-
- Seeman TE (1996) Social ties and health: The benefits of social integration. Annals of epidemiology 6: 442–451. - PubMed
-
- Bondevik M, Skogstad A (1998) The oldest old, ADL, social network, and loneliness. Western Journal of Nursing Research 20: 325–343. doi: 10.1177/019394599802000305 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Francis D (1991) Friends from the workplace. Growing old in America: 465–480.
-
- De Vogli R, Chandola T, Marmot MG (2007) Negative aspects of close relationships and heart disease. Archives of Internal Medicine 167: 1951–1957. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.18.1951 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cattan M, White M, Bond J, Learmouth A (2005) Preventing social isolation and loneliness among older people: a systematic review of health promotion interventions. Ageing and society 25: 41–67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

