Influence of coronary architecture on the variability in myocardial infarction induced by coronary ligation in rats
- PMID: 28837679
- PMCID: PMC5570270
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183323
Influence of coronary architecture on the variability in myocardial infarction induced by coronary ligation in rats
Abstract
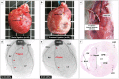
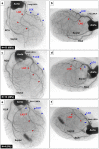
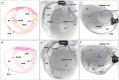
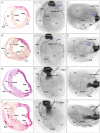
It has been shown that the size of myocardial infarction in rats created by coronary ligation technique is not uniform, varying from 4% to 65%. We hypothesized that infarct size variability induced by coronary artery ligation might be caused by coronary artery branching pattern. Coronary artery angiography was performed in 50 normal Lewis rats and in chronic myocardial infarction models in which coronary artery was ligated immediately below the left atrial appendage or 2mm distal to the left atrial appendage (n = 25 for each), followed by histological analysis. Unlike the human, the rats had a single major septal artery arising from the proximal part of the left coronary artery (n = 30) or right coronary artery (n = 20). There were three branching patterns of left circumflex artery (LCX): 33 (66%) had LCX branching peripherally from a long left main coronary artery (LMCA), while the remainder 17 (34%) had the LCX branching from the proximal part of the septal artery or a short LMCA. The rats with distal coronary ligation presented myocardial infarction localized to an anterior territory irrespective of LCX branching pattern. In the rats with proximal coronary ligation, 64% (n = 16) had broad myocardial infarction involving the anterior and lateral territories, while the remainder (36%, n = 9) had myocardial infarction localized to an anterior territory with the intact LCX arising proximally from a short LMCA. The interventricular septum was spared from infarction in all rats because of its anatomical location. Infarct size variations were caused not only by ligation site but also by varying LCX branching patterns. There are potential risks to create different sizes of myocardial infarction, particularly when targeting a broad range of myocardial infarction. The territory of the septal artery always appears to be spared from myocardial infarction induced by the coronary ligation technique.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct mouse coronary anatomy and myocardial infarction consequent to ligation.Coron Artery Dis. 2005 Feb;16(1):41-4. doi: 10.1097/00019501-200502000-00008. Coron Artery Dis. 2005. PMID: 15654199
-
Single-stent crossover technique from distal unprotected left main coronary artery to the left circumflex artery.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Nov 1;82(5):757-64. doi: 10.1002/ccd.24988. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013. PMID: 23674385
-
Microvascular Dysfunction Related to Progressive Left Ventricular Remodeling due to Chronic Occlusion of the Left Anterior Descending Artery in an Adult Porcine Heart.Int Heart J. 2019 May 30;60(3):715-727. doi: 10.1536/ihj.18-346. Epub 2019 May 17. Int Heart J. 2019. PMID: 31105143
-
The role of septal perforators and "myocardial bridging effect" in atherosclerotic plaque distribution in the coronary artery disease.Pol J Radiol. 2015 Apr 16;80:195-201. doi: 10.12659/PJR.893227. eCollection 2015. Pol J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25922625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental myocardium infarction in rats: analysis of the model.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2009 Oct;93(4):434-40, 426-32. doi: 10.1590/s0066-782x2009001000018. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19936465 Review. English, Portuguese, Spanish.
Cited by
-
Mitigation of Fibrosis after Myocardial Infarction in Rats by Using a Porcine Cholecyst Extracellular Matrix.Comp Med. 2023 Aug 27;73(4):312-323. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-22-000097. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Comp Med. 2023. PMID: 37527924 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Myocardial Infarction Effects of Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata Extracts and Their Influence on Small Molecules in the Heart Using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Mass Spectrometry Imaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 29;20(19):4837. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194837. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31569464 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical prospects and challenges of photothermal nanomaterials in myocardium recovery after myocardial infarction.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 29;12:1491581. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1491581. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39539693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The right coronary artery in the heart of chinchilla (Chinchilla laniger Molina).Vet Res Commun. 2023 Jun;47(2):745-752. doi: 10.1007/s11259-022-10035-4. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Vet Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 36380084 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal ultrasound imaging of a rat model with ischemic heart failure and its relationship to histopathology.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Sep 15;16(9):4589-4600. doi: 10.62347/FIWE8677. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39398608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klocke R, Tian W, Kuhlmann MT, Nikol S. Surgical animal models of heart failure related to coronary heart disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;74:29–38. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.11.026 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Geltman EM, Ehsani AA, Campbell MK, Schechtman K, Roberts R, Sobel BE. The influence of location and extent of myocardial infarction on long-term ventricular dysrhythmia and mortality. Circulation 1979; 60: 805–814. - PubMed
-
- Maclean D, Fishbein MC, Braunwald E, Maroko PR. Long-term preservation of ischemic myocardium after experimental coronary artery occlusion. J Clin Invest 197861: 541–551. doi: 10.1172/JCI108965 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wilson RB, Hartroft WS. Pathogenesis of myocardial infarcts in rats fed a thrombogenic diet. Arch Pathol 1970;89:457–469. - PubMed
-
- Liu YH, Yang XP, Nass O, Sabbah HN, Peterson E, Carretero OA. Chronic heart failure induced by coronary artery ligation in Lewis inbred rats. Am J Physiol 1997;272:722–727. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

