The role of mineralocorticoid receptor signaling in the cross-talk between adipose tissue and the vascular wall
- PMID: 28838041
- PMCID: PMC5852511
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvx097
The role of mineralocorticoid receptor signaling in the cross-talk between adipose tissue and the vascular wall
Abstract
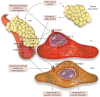
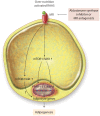
Vascular dysfunction and impaired endothelial mediated relaxation are powerful underlying abnormalities in the pathogenesis of hypertension, coronary heart disease, and stroke. Obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and other metabolic abnormalities are associated with activation of mineralocorticoid receptor (MRs) in the vasculature and adipose tissue. While MR signaling is involved in the normal physiological differentiation and maturation of adipocyte, enhanced activation of MRs also contributes to increase oxidative stress, release of pro-inflammatory adipokines, and dysregulation of adipocyte autophagy. This, in turn, increases the maladaptive expansion of subcutaneous, visceral and perivascular adipose tissue, resulting in systemic and cardiovascular (CV) insulin resistance and increased CV stiffness and impaired vascular and cardiac relaxation. This review summarizes the normal role of MR activation in adipose tissues and explores the mechanisms by which excessive MR activation mediates adipose tissue inflammation and vascular dysfunction. Potential preventative and therapeutic strategies directed in the prevention of MR activation and CV disease are also discussed.
Keywords: Adipocyte tissue; Adipokines; Cardiovascular disease; Metabolic disorders; Mineralocorticoid receptors; Obesity.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author 2017. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Ivanes F, Susen S, Mouquet F, Pigny P, Cuilleret F, Sautiere K, Collet JP, Beygui F, Hennache B, Ennezat PV, Juthier F, Richard F, Dallongeville J, Hillaert MA, Doevendans PA, Jude B, Bertrand M, Montalescot G, Van Belle E.. Aldosterone, mortality, and acute ischaemic events in coronary artery disease patients outside the setting of acute myocardial infarction or heart failure. Eur Heart J 2012;33:191–202. - PubMed
-
- Shen JZ, Young MJ.. Corticosteroids, heart failure, and hypertension: a role for immune cells? Endocrinology 2012;153:5692–5700. - PubMed
-
- Glicklich D, Frishman WH.. Drug therapy of apparent treatment-resistant hypertension: focus on mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. Drugs 2015;75:473–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

