C4 Nephritic Factors in C3 Glomerulopathy: A Case Series
- PMID: 28838767
- PMCID: PMC5701858
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.07.004
C4 Nephritic Factors in C3 Glomerulopathy: A Case Series
Abstract
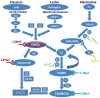
Background: C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) defines a group of rare complement-mediated kidney diseases with a shared underlying pathophysiology: dysregulation of complement in the fluid phase and glomerular microenvironment. Dysregulation can be driven by autoantibodies to C3 and C5 convertases.
Study design: Case series.
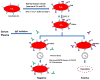
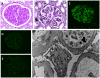
Setting & participants: 168 patients with C3G (dense deposit disease, 68; C3 glumerulonephritis, 100) selected from our C3G biobank.
Outcomes: Patient-purified immunoglobulin Gs were tested for C4 nephritic factors (C4NeFs). These autoantibodies recognize C4b2a, the C3 convertase of the classical pathway of complement.
Measurements: C4NeFs were detected using a modified hemolytic assay.
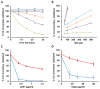
Results: C4NeFs were identified in 5 patients, 4 of whom had C3 glomerulonephritis. C4NeFs were associated with dysregulation of C3 and C5 convertases, and they appear to stabilize these convertases in a dose-dependent manner. C4NeFs also appear to protect C4b2a from decay mediated by soluble CR1 and C4 binding protein. The stabilizing activity of the autoantibodies was further demonstrated by using heat treatment to inactivate complement. C4NeFs were not detected in 150 patients with another complement-mediated kidney disease, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. They were also absent in 300 apparently healthy controls.
Limitations: In addition to C4NeFs, 2 patients had positive findings for other autoantibodies: one patient also had autoantibodies to factor H; the other patient also had autoantibodies to C3bBb (C3NeFs).
Conclusions: The finding of C4NeFs in a small percentage of patients with C3G highlights the challenge in identifying autoantibodies that drive complement dysregulation and underscores the complexity of the autoantibody repertoire that can be identified in these patients.
Keywords: C3 glomerulonephritis; C3 glomerulopathy (C3G); C3 nephritic factors (C3NeFs); C4 nephritic factors (C4NeFs); autoantibodies; case series; complement dysregulation; complement-mediated renal disease; dense deposit disease (DDD); immune deposits; kidney biopsy.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Xiao X, Ghossein C, Tortajada A, et al. Familial C3 glomerulonephritis caused by a novel CFHR5-CFHR2 fusion gene. Mol Immunol. 2016;77(9):89–96. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

