High-Resolution Maps of Mouse Reference Populations
- PMID: 28839117
- PMCID: PMC5633391
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.117.300188
High-Resolution Maps of Mouse Reference Populations
Abstract
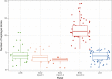
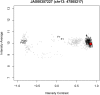
Genetic reference panels are widely used to map complex, quantitative traits in model organisms. We have generated new high-resolution genetic maps of 259 mouse inbred strains from recombinant inbred strain panels (C57BL/6J × DBA/2J, ILS/IbgTejJ × ISS/IbgTejJ, and C57BL/6J × A/J) and chromosome substitution strain panels (C57BL/6J-Chr#<A/J>, C57BL/6J-Chr#<PWD/Ph>, and C57BL/6J-Chr#<MSM/Ms>). We genotyped all samples using the Affymetrix Mouse Diversity Array with an average intermarker spacing of 4.3 kb. The new genetic maps provide increased precision in the localization of recombination breakpoints compared to the previous maps. Although the strains were presumed to be fully inbred, we found residual heterozygosity in 40% of individual mice from five of the six panels. We also identified de novo deletions and duplications, in homozygous or heterozygous state, ranging in size from 21 kb to 8.4 Mb. Almost two-thirds (46 out of 76) of these deletions overlap exons of protein coding genes and may have phenotypic consequences. Twenty-nine putative gene conversions were identified in the chromosome substitution strains. We find that gene conversions are more likely to occur in regions where the homologous chromosomes are more similar. The raw genotyping data and genetic maps of these strain panels are available at http://churchill-lab.jax.org/website/MDA.
Keywords: chromosome substitution strains; gene conversions; mouse diversity genotyping array; recombinant inbred strains.
Copyright © 2017 Simecek et al.
Figures

References
-
- Beck J. A., Lloyd S., Hafezparast M., Lennon-Pierce M., Eppig J. T., et al. , 2000. Genealogies of mouse inbred strains. Nat. Genet. 24: 23–25. - PubMed
-
- Belknap J., 1998. Effect of within-strain sample size on QTL detection and mapping using recombinant inbred mouse strains. Behav. Genet. 28: 29–38. - PubMed
-
- Broman K. W., Sen S., 2009. A Guide to QTL Mapping with R/qtl. Springer, New York.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
