Standardization of DNA Residual Quantification Method of Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine for Human Use
- PMID: 28839473
- PMCID: PMC5543725
- DOI: 10.2174/1874104501711010066
Standardization of DNA Residual Quantification Method of Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine for Human Use
Abstract
Objectives: Normalize the quantification of residual DNA from Vero cells in the rabies vaccine for use in human VAHV I, by quantitative PCR in real time and the design of primers that amplified, highly repetitive sequences of Cercopithecus aethiops and a constitutive gene according to sequences reported in the GenBank and quantifying the residual DNA in the vaccine VAHV I in three consecutive batches according to the standard set by the World Health Organization.
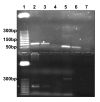
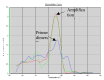
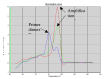
Methods: A real time quantitative method based on SYBR Green chemistry has been applied for the quantification of residual DNA (resDNA) using highly repetitive DNA (Alu) and a housekeeping gene (B-actin) as target sequences.
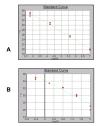
Results: The sensitivity achieved with this white sequence is within the reported limits and who are between 5 and 50 pg. For real time PCR optimization with Alu-p53, different concentrations of MgCl2 (0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25 and 1.5 mm) in combination with three different concentrations of primers (75, 100 and 150nM) were used. pDNA in concentration of 1x107 copies / ul was used as template. Optimal concentrations were 1.25 mM MgCl2 and 100nM primers. To level of detection of 1.53 ng/ul was found for p53-Alu and Alu-Glob and 0.39 ng/ul for B-actin with gDNA curves.
Conclusion: Quantification of resDNA of vaccine VAHV I with close-ups of B-actin was normalized. Reached a sensitivity of 30 pg of resDNA/dose VAHV I, with close-ups of B-actin. Found, in three consecutive batches, an amount less than 10 ng/dose, these results suggest that the production process ensures vaccine resDNA removal, meeting international requirements for biological products for use in humans that use continuous cell lines for production.
Keywords: Antirrabic vaccine; Betapropiolactone; Real time PCR; Residual DNA; Vero cells.
Figures






References
-
- Belotto A., Schneider M.C., Leanes L.F., Correa E., Tamayo H., Fernández E. Situación actual de la rabia en América Latina. Organización Panamericana de la Salud; 2003.
-
- Muniappan B., Thilly W. PCR assay to detect Vero cell DNA in vaccines. MIT. Cambridge, MA, USA : Center for Environmental Health Sciences and Division of Toxicology.; 1996.
-
- Lokteff M., Klinguer-Hamour C., Julien E., Picot D., Lannes L., Nguyen T., Bonnefoy J.Y., Beck A. Residual DNA quantification in clinical batches of BBG2Na, a recombinant subunit vaccine against human respiratory syncytial virus. Biologicals. 2001;29(2):123–132. doi: 10.1006/biol.2001.0283. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
